UNIDAD: 11.- LOS ANIMALES.
|
|
|
- Soledad Pereyra Vega
- hace 9 años
- Vistas:
Transcripción
1 UNIDAD: 11.- LOS ANIMALES. CARACTERÍSTICAS DE LOS ANIMALES. Características generales: Son seres pluricelulares, con células eucariotas. Funciones vitales: - Nutrición: La alimentación es heterótrofas. Como son muy activos, necesitan mucha energía, por tanto tiene que tener aparatos y sistemas muy efectivos. Estos aparatos son: aparato digestivo, aparato circulatorio, aparato respiratorio y aparato excretor. - Relación: Los animales se mueven, cazan, se defienden, etc. Para ello necesitan relacionarse bien con el medio. Tienen los órganos de los sentidos, el sistema nervioso y el sistema locomotor muy bien desarrollados. - Reproducción: Tienen reproducción sexual, aunque algunos animales muy simples también se pueden reproducir asexualmente. Sexos: Son normalmente machos o hembras, pero hay algunos que son hermafroditas, estos animales se pueden fecundar mutuamente. La fecundación: Puede ser interna (los óvulos son fecundados dentro del aparato reproductor femenino) o externa (los óvulos son fecundados fuera del aparato reproductor femenino). El desarrollo embrionario: Puede ser vivíparos (se desarrollan en el útero materno), ovíparos (se desarrollan dentro del huevo) o ovovivíparos (se desarrollan en un huevo, pero se incuban dentro del cuerpo de la madre). Clasificación de los animales: Los animales se clasifican en: vertebrados e invertebrados. ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS. Dónde Tipo de viven? reproducción Características generales Ejemplos PORÍFEROS CNIDARIOS PLATELMINTOS (gusanos planos) NEMATODOS (gusanos cilíndricos) ANÉLIDOS MOLUSCOS ARTRÓPODOS (1) Son acuáticos. Viven fijos en el fondo Son acuáticos. Parásitos en el intestino Aguas y sitios húmedos, y en el intestino. Acuáticos o terrestres Acuáticos o terrestres Acuáticos o terrestres EQUINODERMOS Marinos - Tienen poros conectados con la cavidad central. - No tienen verdaderos tejidos - Tienen un armazón que los mantiene erguidos. - Viven fijos o nadan libremente - La boca está rodeada de tentáculos. - Tienen verdaderos tejidos, pero no órganos especializados. - Son sensibles al contacto y puede contraerse y moverse. - Tienen células venenosas. - Tienen órganos sencillos, pero carecen de aparatos - Cuerpo aplanado - Tienen órganos sencillos, pero carecen de aparatos - Cuerpo cilíndrico - Tienen tubo digestivo con boca y ano - Forma de gusanos - Su cuerpo está dividido en anillos - Cabeza bien definida con boca y tentáculos - Tienen ojos rudimentarios y mandíbulas en algunos casos - Tienen órganos que forman aparatos especializados - Órganos y sistemas desarrollados - La mayoría tiene cabeza y pie - Tienen concha, aunque algunos tienen una pequeña pluma interna - Cuerpo dividido en segmento - Pueden tener patas, alas, antenas, etc. - tiene caparazón duro articulado (exoesqueleto) - Mudan para crecer - Tienen aparatos especializados - Tienen órganos sensoriales muy precisos - Tienen respiración branquial o traqueal - Sufren metamorfosis - Cuerpo redondeado o estrellado - tienen caparazón espinoso - Aparatos y sistemas desarrollados - Tentáculos para moverse (pies ambulacrales) (1) Los grupos más importantes de artrópodos son: arácnidos, crustáceos, miriápodos e insectos Las esponjas Medusas, corales, actinias, etc. Tenia o solitaria Lombrices intestinales Lombriz de tierra, sanguijuela, etc. Caracol, almeja, pulpo, etc. Gambas, cangrejos, arañas, insectos, etc. Estrellas de mar, erizos de mar, etc.
2 CARACTERÍSTICAS DE LOS VERTEBRADOS. - Características generales: Son seres pluricelulares, con células eucariotas, aparatos bien desarrollados y reproducción sexual. Tienen esqueleto interno con columna vertebral y cráneo. Tienen cabeza, tronco y extremidades. ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS. PECES ANFIBIOS REPTILES AVES MAMÍFEROS Dónde viven? Son acuáticos. Desarrollo embrionario Ovíparos (con fecundación interna) Extremidades Son Ovíparos (con terrestres o 4 patas (con metamorfosis y membrana acuáticos. fecundación interdigital) externa) Son terrestres. Son terrestres voladores Son terrestres (algunos acuáticos o voladores) Ovíparos (con fecundación interna) Ovíparos (con fecundación interna) Vivíparos (con fecundación interna) Piel Respiración aletas Escamas Branquias 4 patas (algunos sin patas) 2 alas y 2 patas Muy fina Escamas corneas Plumas - Pulmones - Branquias - Cutánea Pulmones Pulmones 4 patas Pelos pulmones Temp. corporal Sangre fría (poiquilotermos) Sangre fría (poiquilotermos) Sangre fría (poiquilotermos) Sangre caliente (homeotermos) Sangre caliente (homeotermos) Otras características -Forma hidrodinámica -Potente musculatura -Cabeza sin cuello -Ojos con párpados -Boca con mandíbulas y dientes -orificio para el oído -Cabeza con cuello -Ojos y fosas nasales -orificio para el oído - Boca con mandíbulas y dientes -Huesos ligeros -Pueden tener garras -Cuello flexible -Ojos con parpados y fosas nasales -orificio para el oído -Pico córneo -Cabeza con cuello muy móvil -Ojos con párpados -con orejas - Mandíbula con dientes especializados. -Las crías maman leche de sus madres Ejemplos Besugo, tiburón, etc. Rana, salamandra, tritones, etc. Cocodrilos, tortugas, serpientes, etc. Golondrina, águila, etc. Gato, perro, jirafa, león, ser humano, etc.
3 NAME: DATE: 1º ESO (Bilingual) UNIT: 11.- ANIMALS. ANIMAL CHARACTERISTICS. General characteristics: They are multi-cellular beings, with eukaryotic cells. Vital functions: - Nutrition: The feeding is heterotrophic. As they are very active, they need a lot of energy, therefore they have apparatuses and very effective systems, these apparatuses are: digestive system, circulatory system, respiratory system and excretory system. - Relationship: Animals move, hunt, defend themselves, etc. For this, they need to be well adapted with the environment. They have their sensory organs, nervous system and locomotive system very well developed - Reproduction: They have sexual reproduction, although some very simple animals can also reproduce asexually. Sexes: They are normally male or female, but there are some animals that are hermaphrodite, these animals can perform mutually fertilize one another. Fertilization: Can be internal (the eggs are fertilized within the female reproductive system) or external (the eggs are fertilized outside of the female reproductive system). Embryonic development: It can be viviparous (they are developed in the maternal uterus), oviparous (they are developed inside the egg) or ovoviviparous (they are developed in an egg, but they are incubated inside the mother's body) Classification of animals: Animals are classified into: vertebrates and invertebrates. 1.- Copy the information about vital functions : 2.- Translate these words: Multi-cellular beings: Oviparous: Prokaryote: Embryonic development: Fecundation: Vital functions: 3.- How are the animals classified? 4.- What are the different types of fertilization?: 5.- What are the different ways that animals reproduce?
4 6.- Complete: Relationship:, hunt, defend, etc. For this, they need well. They have, and very well. 7.- Write a T if the phrase is true and a F if the phrase is false a) Animals need a lot of energy. b) Animals don t have apparatuses and very effective systems. c) Some very simple animals can reproduce asexually. d) Hermaphrodite animals can undergo metamorphosis. e) Fertilization can be internal or external. f) Animals can be viviparous, oviparous or ovoviviparous. g) Animals are classified into: invertebrates and vertebrates. 8.- What are the possible sexes of animals? 9.- Label each picture: viviparous, oviparous or ovoviviparous Write a brief summary of three vital functions
5 NAME: DATE: 1º ESO (Bilingual) INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS. PORIFERA CNIDARIANS PLATYHEL- MINTHES ( plane worms) NEMATODES (cylindrical worms) ANNELIDS MOLLUSCS ARTHROPODS (1) Where do they live? Aquatics. They live fixed on the bottom of the sea Aquatics. Parasites in the intestine Water and humid places, and in the intestine Aquatic or terrestrial Aquatic or terrestrial Aquatic or terrestrial ECHINODERMS Marines Type of reproduction 1.- Copy the general characteristics of arthropods in the box: General characteristics - They have connected pores with the central cavity. - They do not have true tissues. - They have a frame that maintains them erect. - They live fixed or they swim freely. - The mouth is surrounded by tentacles. - They have true tissues, but not specialized organs. - They are sensitive to touch and can contract and move - They have poisonous cells. - They have simple organs, but they lack apparatuses - Body smoothed. - They have simple organs, but they lack apparatuses. - Cylindrical body. - They have alimentary canal with mouth and anus - Form of worms. - Their body is divided into rings. - Very defined head with mouth and tentacles. - They have rudimentary eyes and jaws in some cases. - They have organs that form specialized apparatuses. - Organs and developed systems. - Most has head and "foot" - They have shell, although some have a small internal eathers. - Body divided into segments. - They can have legs, wings, antennas, etc. - They have an articulate hard shell (exoskeleton ). - They shed to grow. - They have specialized apparatuses. - They have very precise sensory organs. - They have branchial or tracheal breathing. - They suffer metamorphosis. - Rounded or starry body. - They have thorny shell. - Apparatuses and developed systems. - Tentacles to move (ambulacral feet) (1) The most important groups of arthropods are: arachnids, crustaceaus, millipodes and insects Examples The sponges Jellyfishes, corals, actinias, etc. Taenia or solitary Roundworms Earth worm, leech, etc. Snail, clam, octopus, etc. Shrimps, crabs, spiders, insects, etc Starfish, sea urchins, etc 2.- Translate: Starry body: Branchial. Breathing: Wings: Tentacles: Tracheal breathing: Mouth and anus: Metamorphosis: Poisonous cells: Tentacles: 3.- Write down the groups of animals with asexual reproduction: 4.- Write down the groups of animals that only reproduce by the sexual mode:
6 5.- Write down below each picture the word that corresponds (PORIFERA, CNIDARIAN, PLATYHELMINTHE, NEMATODE, ANNELID, MOLLUSC, ARTHROPOD, ECHINODERM,) 6.- Match with arrows: PORIFERA CNIDARIAN PLATYHELMINTHE NEMATODE 7.- Match with arrows: ANNELID MOLLUSC ARTHROPOD ECHINODERM 8.- Which are the most important groups of arthropods?: 9.- Which group of animal is: a) It is an animal: aquatic, sexual or asexual; and does not have true tissues. b) It is an animal: aquatic or terrestrial, sexual; and has organs and a developed system Which group of animal is: a) It is an animal: aquatic, sexual or asexual; and has apparatuses and a developed system. b) It is an animal: aquatic or terrestrial, sexual or asexual; and their body is divided into rings.
7 NAME: DATE: 1º ESO (Bilingual) CHARACTERISTICS OF VERTEBRATES. General characteristics: They are multi-cellular beings, with eukaryotic cells, well-developed apparatuses and sexual reproduction. They have an internal skeleton with a spine and a skull. They have a head, trunk and extremities. 1.- Copy this information: 2.- Translate these words: reproduction: Multi-cellular beings: Skeleton: Trunk: skull: Vertebrates: 3.- Write the general characteristic of vertebrates. 4.- Complete: General characteristics: They are, with cells. Apparatuses and reproduction. They have internal with and. They have, and. 5.- Write a T if the phrase is true and a F if the phrase is false a) Vertebrates are unicellular beings, with eukaryotic cells. b) Vertebrates have sexual reproduction. c) Vertebrates have an internal skeleton. d) Vertebrates have a head, trunk and extremities. e) Notochord is a rigid and flexible cord. 6.- Match these columns with arrows: Invertebrates Vertebrates They are multi-cellular beings They have sexual reproduction They have vertebras. They don t have vertebrae They have a skeleton They have a skull They have well-developed apparatuses They have eukaryotic cells
8 7.- Match these columns with arrows: Vertebrate Invertebrate 8.- What is the main characteristic of vertebrates? 9.- a) Are there any unicellular vertebrate?: b) Are there any vertebrate without a skull? 10.- Underline the most correct phrase: unicellular being a) Vertebrates are multi-cellular being can be unicellular or multi-cellular eukaryotic cells b) Vertebrates have prokaryotic cells eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells non-developed apparatuses c) Vertebrates have a little developed apparatuses Well-developed apparatuses internal skeleton with spine d) Vertebrates have internal skeleton with skull internal skeleton spine and skull head e) Vertebrates have head and extremities extremities, trunk and head
9 NAME: DATE: 1º ESO (Bilingual) VERTEBRATE ANIMALS. FISH AMPHIBIANS Where do they live? Aquatic. REPTILES Terrestrial BIRDS MAMMALS Embryonic develop Oviparous (with internal fertilization) Oviparous Aquatic or (with 4 legs (with terrestrial. metamorphosis interdigital and external membrane) fertilization) Oviparous (with internal fertilization) Are Oviparous terrestrial (with internal flyers fertilization) Terrestrial (some aquatic ones or flyers) Viviparous (with internal fertilization) Skin Fins Scale Gills 4 legs (some without legs) 2 wings and 2 legs Very fine Horny scale Breathing - Lungs - Gills - Cutaneous Lungs Feathers Lungs 4 paws Hair Lungs 1.- Copy all characteristics of mammals in the box: Temp. bodily Extremities Coldblooded (poikilotherms) Coldblooded (poikilotherms) Coldblooded (poikilotherms) Warmblooded (homoio -therms) Warmblooded (homoio -therms) Other characterístics - Hydrodynamic forms - Potent musculature - Head without neck - Eyes with lids - Mouth with jaws and teeth - Hole for hearing - Head with neck - Eyes and nasal cavities - Hole for hearing - Mouth with jaws and teeth - Light bones - They can have claws - Flexible neck - Eyes with lids and nasal cavitiess - Hole for hearing - Horny beak - Head with very mobile neck - Eyes with lids - Ears for hearing - Jaw with specialized teeth - The babies suckle their mothers milk Examples Sea bream, shark, etc. Frog, salamander, newts, etc. Crocodiles, turtles, snakes, etc. Swallow, eagle, etc. Cat, dog, giraffe, lion, human being, etc. 2.- Translate these words: Viviparous: Hot blood: Scale: Oviparous: Cold blood: Gills: Wings: Lungs: Paw: Skin: Fins: Feathers: 3.- What are the general characteristics of birds?:
10 4.- What are the general characteristic of this animal? What kind of animal is it? 5.- What are the general characteristic of this animal? What kind of animal is it? 6.- Complete: a) : Are terrestrial, oviparous with wings. b) : Are homoiotherms, have lungs and hair. c) : Are poikilotherms, have gills and fins. d) : Are oviparous, are cold-blooded and have very thin skin. e) : Are terrestrial, viviparous and have eyes with lids. f) : Are homoiotherms, have lungs and feathers. g) : Are oviparous, have 4 paws, poikilotherms and horny scales. h) : Have 4 paws, internal fecundation. 7.- a) Write five fish:,,,,. b) Write five amphibians:,,,,. c) Write five reptiles:,,,,. 8.- a)write five birds:,,,,. b)write one flyer mammal: c) Write two aquatic mammals:,
11 9.- Write fifteen mammals: 10.- Label each picture with the corresponding word (FISH, AMPHIBIAN, REPTILE, BIRD, MAMMAL )
Module 1: Animals. Natural Sciences 3
 Module 1: Animals Natural Sciences 3 Vertebrates and Invertebrates There are many different animals(hay muchos @pos de animales): Vertebrates (Vertebrados): They have spine (backbone). (Tienen columna
Module 1: Animals Natural Sciences 3 Vertebrates and Invertebrates There are many different animals(hay muchos @pos de animales): Vertebrates (Vertebrados): They have spine (backbone). (Tienen columna
Invertebrados. Vertebrados
 Unidad 9: LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS. 1.- EL REINO ANIMAL. 1.1.- Características de los animales. Los animales presentan las siguientes características: Crecimiento limitado, al contrario que las plantas.
Unidad 9: LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS. 1.- EL REINO ANIMAL. 1.1.- Características de los animales. Los animales presentan las siguientes características: Crecimiento limitado, al contrario que las plantas.
1. The Animal Kingdom
 Animals Unit 11 1. The Animal Kingdom Agrupa a los seres vivos pluricelulares, formados por células eucariotas animales y con nutrición heterótrofa. Los animales se han dividido tradicionalmente en: VERTEBRATES
Animals Unit 11 1. The Animal Kingdom Agrupa a los seres vivos pluricelulares, formados por células eucariotas animales y con nutrición heterótrofa. Los animales se han dividido tradicionalmente en: VERTEBRATES
SCIENCES EXAM Number: 4.1 Last Name/First Name: Group: Date:
 SCIENCES EXAM Number: 4.1 Last Name/First Name: Group: Date: Orthography: Syntax: Global: PART 1 1. Write three differences between the animals shown in the pictures (2 points). Escribe tres diferencias
SCIENCES EXAM Number: 4.1 Last Name/First Name: Group: Date: Orthography: Syntax: Global: PART 1 1. Write three differences between the animals shown in the pictures (2 points). Escribe tres diferencias
TEMA 10.-LOS ANIMALES
 TEMA 10.-LOS ANIMALES Los animales se clasifican en dos grupos: vertebrados e invertebrados. Los animales vertebrados son los que tienen esqueleto (huesos). Todos los demás animales están dentro del grupo
TEMA 10.-LOS ANIMALES Los animales se clasifican en dos grupos: vertebrados e invertebrados. Los animales vertebrados son los que tienen esqueleto (huesos). Todos los demás animales están dentro del grupo
LOS ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS E INVERTEBRADOS
 LOS ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS E INVERTEBRADOS Ahora vamos a clasificar a los animales según si tienen esqueleto o no. Los VERTEBRADOS son animales que tienen esqueleto. El esqueleto puede estar formado por
LOS ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS E INVERTEBRADOS Ahora vamos a clasificar a los animales según si tienen esqueleto o no. Los VERTEBRADOS son animales que tienen esqueleto. El esqueleto puede estar formado por
Clasificación de los animales
 Clasificación de los animales Clasificación según su alimentación: Los animales que se alimentan de otros animales son carnívoros. Los animales que se alimentan de raices, semillas, tallos, hojas o frutos
Clasificación de los animales Clasificación según su alimentación: Los animales que se alimentan de otros animales son carnívoros. Los animales que se alimentan de raices, semillas, tallos, hojas o frutos
UNIDAD 2 - LOS ANIMALES. Bloque 1: Cómo son los animales
 UNIDAD 2 - LOS ANIMALES Bloque 1: Cómo son los animales 1. Los animales pueden ser muy diferentes entre sí, sin embargo, comparte algunas características en cuanto a organización del cuerpo. Cuáles son
UNIDAD 2 - LOS ANIMALES Bloque 1: Cómo son los animales 1. Los animales pueden ser muy diferentes entre sí, sin embargo, comparte algunas características en cuanto a organización del cuerpo. Cuáles son
Conocimiento del Medio Natural, Social y Natural UNIDAD 3. Los animales FICHA 3.1
 UNIDAD 3. Los animales FICHA 3.1 1. Indica si los siguientes animales son vertebrados o invertebrados: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) 2. Indica si los siguientes animales son ovíparos o vivíparos:
UNIDAD 3. Los animales FICHA 3.1 1. Indica si los siguientes animales son vertebrados o invertebrados: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) 2. Indica si los siguientes animales son ovíparos o vivíparos:
Reino Animal (Animalia, Metazoa)
 Reino Animal (Animalia, Metazoa) El reino animal (Animalia o Metazoa) consiste en organismos heterótrofos, es decir, aquellos que no producen su propio alimento, y por lo tanto una característica muy llamativa
Reino Animal (Animalia, Metazoa) El reino animal (Animalia o Metazoa) consiste en organismos heterótrofos, es decir, aquellos que no producen su propio alimento, y por lo tanto una característica muy llamativa
Natural Sciences 4. Module 1: Living Things
 Natural Sciences 4 Module 1: Living Things Kingdoms To make the study easier we divide them into kingdoms. (Para estudiarlos con mayor facilidad dividimos los seres vivos en reinos). The Animal, Plant
Natural Sciences 4 Module 1: Living Things Kingdoms To make the study easier we divide them into kingdoms. (Para estudiarlos con mayor facilidad dividimos los seres vivos en reinos). The Animal, Plant
Los Invertebrados LOS INVERTEBRADOS
 LOS INVERTEBRADOS 1 Los animales invertebrados, al igual que todas los seres vivos, realizan las tres funciones vitales: nutrición, relación y reproducción. Función de nutrición. Los órganos y aparatos
LOS INVERTEBRADOS 1 Los animales invertebrados, al igual que todas los seres vivos, realizan las tres funciones vitales: nutrición, relación y reproducción. Función de nutrición. Los órganos y aparatos
REINO ANIMAL INTRODUCCIÓN
 REINO ANIMAL INTRODUCCIÓN CLASIFICACIÓN SERES VIVOS CLASIFICACIÓN SERES VIVOS - REINOS 1. Archaea (Arqueas) 2. Bacteria 3. Protista (Protozoos) 4. Fungi (Hongos) MONERAS 5. Plantae (Plantas, Metafitos)
REINO ANIMAL INTRODUCCIÓN CLASIFICACIÓN SERES VIVOS CLASIFICACIÓN SERES VIVOS - REINOS 1. Archaea (Arqueas) 2. Bacteria 3. Protista (Protozoos) 4. Fungi (Hongos) MONERAS 5. Plantae (Plantas, Metafitos)
Biología Especies de Metazoos
 Biología Especies de Metazoos Las esponjas Animales marinos invertebrados sencillos. Forma redondeada y con numerosos poros. La estructura de las esponjas está formada por numerosas y pequeñas cavidades
Biología Especies de Metazoos Las esponjas Animales marinos invertebrados sencillos. Forma redondeada y con numerosos poros. La estructura de las esponjas está formada por numerosas y pequeñas cavidades
Biología METAZOOS. Tienen esqueleto interior formado de sílice o de carbonato cálcico y/o de una proteína llamada espongina (suave al tacto).
 Biología METAZOOS Las esponjas Animales marinos invertebrados sencillos. Forma redondeada y con numerosos poros. La estructura de las esponjas está formada por numerosas y pequeñas cavidades conectadas
Biología METAZOOS Las esponjas Animales marinos invertebrados sencillos. Forma redondeada y con numerosos poros. La estructura de las esponjas está formada por numerosas y pequeñas cavidades conectadas
A los animales con columna vertebral se les llama vertebrados. Los vertebrados tienen mas partes en el cuerpo que los invertebrados.
 A los animales con columna vertebral se les llama vertebrados. Los vertebrados tienen mas partes en el cuerpo que los invertebrados. Cada vertebrado tiene un esqueleto dentro del cuerpo. Un esqueleto es
A los animales con columna vertebral se les llama vertebrados. Los vertebrados tienen mas partes en el cuerpo que los invertebrados. Cada vertebrado tiene un esqueleto dentro del cuerpo. Un esqueleto es
TEMA2. MUCHOS REINOS COMPARTEN EL MEDIO
 TEMA2. MUCHOS REINOS COMPARTEN EL MEDIO CARACTERÍSTICAS DE LOS ANIMALES Se alimentan de otros seres vivos Casi todos pueden desplazarse (ir de un lugar a otro) Algunos animales son ovíparos (nacen de huevos)
TEMA2. MUCHOS REINOS COMPARTEN EL MEDIO CARACTERÍSTICAS DE LOS ANIMALES Se alimentan de otros seres vivos Casi todos pueden desplazarse (ir de un lugar a otro) Algunos animales son ovíparos (nacen de huevos)
UNIDAD 10 Y 11: EL REINO ANIMAL
 UNIDAD 10 Y 11: EL REINO ANIMAL 1. INTRODUCCIÓN Los animales son seres vivos que: tienen células eucariotas. tiene nutrición heterótrofa. están formados por muchas células (pluricelulares). tienen músculos
UNIDAD 10 Y 11: EL REINO ANIMAL 1. INTRODUCCIÓN Los animales son seres vivos que: tienen células eucariotas. tiene nutrición heterótrofa. están formados por muchas células (pluricelulares). tienen músculos
ANIMALES CON ESQUELETO
 ANIMALES CON ESQUELETO LOS ANIMALES pueden ser ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS no son los que se clasifican en UN ESQUELETO INTERNO CON COLUMNA VERTEBRAL COLUMNA VERTEBRAL MAMÍFEROS PECES ANFIBIOS
ANIMALES CON ESQUELETO LOS ANIMALES pueden ser ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS no son los que se clasifican en UN ESQUELETO INTERNO CON COLUMNA VERTEBRAL COLUMNA VERTEBRAL MAMÍFEROS PECES ANFIBIOS
Qué características tienen los invertebrados? Que no tienen columna vertebral, pero pueden tener exoesqueleto. Se desplazan utilizando los músculos
 Índice 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 portada esquema características de los invertebrados características de los poríferos características de los calentéreos clasificación de los celentéreos caracteristicas
Índice 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 portada esquema características de los invertebrados características de los poríferos características de los calentéreos clasificación de los celentéreos caracteristicas
Bacterias. Algas Verde-azulada
 Bacterias Reino Moneras Microscópicos Formados por una sola célula Reproducción muy sencilla Resistentes al frío, al calor, humedad, etc. Extendidos por toda la tierra. Algas Verde-azulada Reino Protistas
Bacterias Reino Moneras Microscópicos Formados por una sola célula Reproducción muy sencilla Resistentes al frío, al calor, humedad, etc. Extendidos por toda la tierra. Algas Verde-azulada Reino Protistas
Los animales son seres vivos junto con las plantas y los hongos. Todos nacen, crecen, se relaciona, se reproducen y mueren.
 Los animales son seres vivos junto con las plantas y los hongos. Todos nacen, crecen, se relaciona, se reproducen y mueren. Los animales pueden clasificarse en dos grupos: Animales vertebrados: Tienen
Los animales son seres vivos junto con las plantas y los hongos. Todos nacen, crecen, se relaciona, se reproducen y mueren. Los animales pueden clasificarse en dos grupos: Animales vertebrados: Tienen
Además, comparten las siguientes características: o Su cuerpo está dividido en partes: cabeza,
 UNIT 8: Vertebrates UNIDAD 2 VERTEBRATES VERTEBRADOS. CARACTERÍSTICAS DE LOS VERTEBRADOS La principal característica de los vertebrados es que tienen columna vertebral o esqueleto interno con huesos y
UNIT 8: Vertebrates UNIDAD 2 VERTEBRATES VERTEBRADOS. CARACTERÍSTICAS DE LOS VERTEBRADOS La principal característica de los vertebrados es que tienen columna vertebral o esqueleto interno con huesos y
BALOTARIO DE CTA. Resuelve las siguientes actividades en hoja cuadriculada para su respectiva presentación.
 Colegio San Ignacio de Loyola Primero de Secundaria BALOTARIO DE CTA Resuelve las siguientes actividades en hoja cuadriculada para su respectiva presentación. 1.- Elabora un cuadro comparativo y establece
Colegio San Ignacio de Loyola Primero de Secundaria BALOTARIO DE CTA Resuelve las siguientes actividades en hoja cuadriculada para su respectiva presentación. 1.- Elabora un cuadro comparativo y establece
TEMA 11. LOS ANIMALES
 CARACTERÍSTICAS GENERALES CÉLULAS EUCARIOTAS PLURICELULARES CON TEJIDOS VERDADEROS NUTRICIÓN HETERÓTROFA Tipo poríferos Tipo cnidarios o celentéreos Tipo moluscos Tipo anélidos Tipo artrópodos Tipo equinodermos
CARACTERÍSTICAS GENERALES CÉLULAS EUCARIOTAS PLURICELULARES CON TEJIDOS VERDADEROS NUTRICIÓN HETERÓTROFA Tipo poríferos Tipo cnidarios o celentéreos Tipo moluscos Tipo anélidos Tipo artrópodos Tipo equinodermos
TEMA 11. LOS ANIMALES
 CARACTERÍSTICAS GENERALES CÉLULAS EUCARIOTAS PLURICELULARES CON TEJIDOS VERDADEROS NUTRICIÓN HETERÓTROFA Tipo poríferos Tipo cnidarios o celentéreos Tipo moluscos Tipo anélidos Tipo artrópodos Tipo equinodermos
CARACTERÍSTICAS GENERALES CÉLULAS EUCARIOTAS PLURICELULARES CON TEJIDOS VERDADEROS NUTRICIÓN HETERÓTROFA Tipo poríferos Tipo cnidarios o celentéreos Tipo moluscos Tipo anélidos Tipo artrópodos Tipo equinodermos
TEMA 5 INVERTEBRADOS
 TEMA 5 INVERTEBRADOS Cómo son los animales? Cómo son los animales? Eucariotas Cómo son los animales? Eucariotas Pluricelulares (nivel de organización V) Cómo son los animales? Eucariotas Pluricelulares
TEMA 5 INVERTEBRADOS Cómo son los animales? Cómo son los animales? Eucariotas Cómo son los animales? Eucariotas Pluricelulares (nivel de organización V) Cómo son los animales? Eucariotas Pluricelulares
REINO ANIMAL EUCARIONTES PLURICELULARES CÉLULAS SIN PARED CELULAR NUTRICIÓN HETERÓTROFA PRESENCIA DE ESTRUCTURAS SENSORIALES
 REINO ANIMAL EUCARIONTES PLURICELULARES CÉLULAS SIN PARED CELULAR NUTRICIÓN HETERÓTROFA PRESENCIA DE ESTRUCTURAS SENSORIALES REINO ANIMAL Se pueden clasificar atendiendo a diversos criterios: Presencia
REINO ANIMAL EUCARIONTES PLURICELULARES CÉLULAS SIN PARED CELULAR NUTRICIÓN HETERÓTROFA PRESENCIA DE ESTRUCTURAS SENSORIALES REINO ANIMAL Se pueden clasificar atendiendo a diversos criterios: Presencia
Conocimiento del Medio 5º Primaria Tema 2: Animales vertebrados
 1. Los vertebrados Definición Las principales características de los vertebrados son: Poseen un esqueleto interno en el que destaca la columna vertebral, un eje formado por vértebras. Su cuerpo está dividido
1. Los vertebrados Definición Las principales características de los vertebrados son: Poseen un esqueleto interno en el que destaca la columna vertebral, un eje formado por vértebras. Su cuerpo está dividido
COLEGIO AGUSTINIANO CIUDAD SALITRE AREA DE CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EDUCACION AMBIENTAL TALLER PLAN DE MEJORAMIENTO I PERIODO GRADO QUINTO
 COLEGIO AGUSTINIANO CIUDAD SALITRE AREA DE CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EDUCACION AMBIENTAL TALLER PLAN DE MEJORAMIENTO I PERIODO GRADO QUINTO LEE ATENTAMENTE EL SIGUIENTE TEXTO Y SELECCIONA LA RESPUESTA CORRECTA.
COLEGIO AGUSTINIANO CIUDAD SALITRE AREA DE CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EDUCACION AMBIENTAL TALLER PLAN DE MEJORAMIENTO I PERIODO GRADO QUINTO LEE ATENTAMENTE EL SIGUIENTE TEXTO Y SELECCIONA LA RESPUESTA CORRECTA.
ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS. Tema 3. - No tienen columna vertebral. - Algunos tienen protección - Concha. - Grupos - Gusanos (lombriz de tierra )
 ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS Tema 3 - No tienen columna vertebral - Caparazón - Algunos tienen protección - Concha - Piel dura los invertebrados - Todos son ovíparos Nacen de huevos - Moluscos (almeja, pulpo
ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS Tema 3 - No tienen columna vertebral - Caparazón - Algunos tienen protección - Concha - Piel dura los invertebrados - Todos son ovíparos Nacen de huevos - Moluscos (almeja, pulpo
MAMMALS. Mammals are viviparous, except for monotremes, which are oviparous. Los mamíferos son vivíparos, excepto los monotremas, que son ovíparos
 MAMMALS Mammals are viviparous, except for monotremes, which are oviparous. Los mamíferos son vivíparos, excepto los monotremas, que son ovíparos MAMMALS Mammals can be carnivores, herbivores or omnivores.
MAMMALS Mammals are viviparous, except for monotremes, which are oviparous. Los mamíferos son vivíparos, excepto los monotremas, que son ovíparos MAMMALS Mammals can be carnivores, herbivores or omnivores.
PREGUNTAS TEMA 5. Los animales y plantas son seres vivos porque nacen, crecen, se reproducen y mueren. Además realizan las funciones vitales.
 1 PREGUNTAS TEMA 5 1.- Por qué los animales y plantas son seres vivos? Los animales y plantas son seres vivos porque nacen, crecen, se reproducen y mueren. Además realizan las funciones vitales. 2.- En
1 PREGUNTAS TEMA 5 1.- Por qué los animales y plantas son seres vivos? Los animales y plantas son seres vivos porque nacen, crecen, se reproducen y mueren. Además realizan las funciones vitales. 2.- En
REPASO EN ESPAÑOL C.E.I.P. GLORIA FUERTES SCIENCE 4 UNIDAD 3: ANIMALES (ANIMALS) Mamíferos
 REPASO EN ESPAÑOL C.E.I.P. GLORIA FUERTES SCIENCE 4 UNIDAD 3: ANIMALES (ANIMALS) Mamíferos Hay muchas clases de mamíferos. Estos pueden ser muy grandes como las ballenas o los elefantes o muy pequeños
REPASO EN ESPAÑOL C.E.I.P. GLORIA FUERTES SCIENCE 4 UNIDAD 3: ANIMALES (ANIMALS) Mamíferos Hay muchas clases de mamíferos. Estos pueden ser muy grandes como las ballenas o los elefantes o muy pequeños
PREGUNTAS TIPO PARA EL EXAMEN DE LA SEGUNDA PARTE DE RECUPERACIÓN DE PENDIENTES
 PREGUNTAS TIPO PARA EL EXAMEN DE LA SEGUNDA PARTE DE RECUPERACIÓN DE PENDIENTES Asignatura: CIENCIAS DE LA NATURALEZA Curso: 1º ESO Temas: 7, 8, 9, 10 y 11 Examen: día 12 de abril TEMA 7: LOS SERES VIVOS
PREGUNTAS TIPO PARA EL EXAMEN DE LA SEGUNDA PARTE DE RECUPERACIÓN DE PENDIENTES Asignatura: CIENCIAS DE LA NATURALEZA Curso: 1º ESO Temas: 7, 8, 9, 10 y 11 Examen: día 12 de abril TEMA 7: LOS SERES VIVOS
ADAPTACIÓN CURRICULAR LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS
 ADAPTACIÓN CURRICULAR LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS 1. El reino animal 2. Poríferos 3. Cnidarios. Gusanos 5. Moluscos 6. Artrópodos 7. Equinodermos Evaluación Los animales invertebrados. Adaptación curricular
ADAPTACIÓN CURRICULAR LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS 1. El reino animal 2. Poríferos 3. Cnidarios. Gusanos 5. Moluscos 6. Artrópodos 7. Equinodermos Evaluación Los animales invertebrados. Adaptación curricular
Actividades de RECUPERACIÓN 2ª EVALUACIÓN Año 2016/ 17. Nombre y apellidos:... Nº:.
 Actividades de RECUPERACIÓN 2ª EVALUACIÓN Año 2016/ 17 Curso. Nombre y apellidos:..... Nº:. TEMA 5 1).- Completa las frases con las palabras adecuadas relacionadas con las características de los animales:
Actividades de RECUPERACIÓN 2ª EVALUACIÓN Año 2016/ 17 Curso. Nombre y apellidos:..... Nº:. TEMA 5 1).- Completa las frases con las palabras adecuadas relacionadas con las características de los animales:
VERTEBRADOS RECUERDA QUE:
 VERTEBRADOS A continuación te vas a encontrar información sobre LOS ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS basada en el tema que aparece en tu libro de texto. Lee las siguientes instrucciones para que puedas trabajar el
VERTEBRADOS A continuación te vas a encontrar información sobre LOS ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS basada en el tema que aparece en tu libro de texto. Lee las siguientes instrucciones para que puedas trabajar el
U.E COLEGIO "CRISTO REY" PPDOMINICOS. SAN CRISTÓBAL EDO. TÁCHIRA. BIOLOGÍA DE 4TO AÑO. Reino Animal
 U.E COLEGIO "CRISTO REY" PPDOMINICOS. SAN CRISTÓBAL EDO. TÁCHIRA. BIOLOGÍA DE 4TO AÑO. Reino Animal Reino Animal Vertebrados Mamíferos Aves Peces Anfibios Reptiles Invertebrados Artrópodos Insectos Arácnidos
U.E COLEGIO "CRISTO REY" PPDOMINICOS. SAN CRISTÓBAL EDO. TÁCHIRA. BIOLOGÍA DE 4TO AÑO. Reino Animal Reino Animal Vertebrados Mamíferos Aves Peces Anfibios Reptiles Invertebrados Artrópodos Insectos Arácnidos
MUCHOS REINOS COMPARTEN EL MEDIO El reino de los animales. Los invertebrados
 MUCHOS REINOS COMPARTEN EL MEDIO El reino de los animales. Los invertebrados Características de los animales Los animales se alimentan (comen) de otros seres vivos. Casi todos pueden desplazarse (moverse)
MUCHOS REINOS COMPARTEN EL MEDIO El reino de los animales. Los invertebrados Características de los animales Los animales se alimentan (comen) de otros seres vivos. Casi todos pueden desplazarse (moverse)
2- Contesta verdadero (V) o falso (F) a las siguientes afirmaciones: a) Los animales son organismos procariotas y pluricelulares.
 ACTIVIDADES TEMA 11: INVERTEBRADOS 1- Qué son los animales? 2- Contesta verdadero (V) o falso (F) a las siguientes afirmaciones: a) Los animales son organismos procariotas y pluricelulares. b) Los animales
ACTIVIDADES TEMA 11: INVERTEBRADOS 1- Qué son los animales? 2- Contesta verdadero (V) o falso (F) a las siguientes afirmaciones: a) Los animales son organismos procariotas y pluricelulares. b) Los animales
Tema 2: Los animales invertebrados
 Tema 2: Los animales invertebrados Características que identifican a los animales Los animales son organismos pluricelulares, eucariotas y heterótrofos. Nutrición: Los animales al ser organismos heterótrofos
Tema 2: Los animales invertebrados Características que identifican a los animales Los animales son organismos pluricelulares, eucariotas y heterótrofos. Nutrición: Los animales al ser organismos heterótrofos
Reino Animalia: Eucariotas, multicelulares, ingieren su comida. Digestión interna. Tejidos nervioso y muscular son únicos de este reino
 Reino Animalia: Eucariotas, multicelulares, ingieren su comida. Digestión interna Tejidos nervioso y muscular son únicos de este reino Reino Animalia: Luego de la fertilización, el zigoto se divide, dando
Reino Animalia: Eucariotas, multicelulares, ingieren su comida. Digestión interna Tejidos nervioso y muscular son únicos de este reino Reino Animalia: Luego de la fertilización, el zigoto se divide, dando
Nombre: Completa el esquema. La función de nutrición. tiene lugar mediante la. Completa la tabla. Obtener. Obtener el. Eliminar.
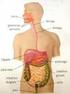 Completa el esquema La función de nutrición tiene lugar mediante la Digestión Circulación Su función es Su función es Su función es Su función es Obtener Nutrientes. Obtener el Oxígeno del aire. Eliminar
Completa el esquema La función de nutrición tiene lugar mediante la Digestión Circulación Su función es Su función es Su función es Su función es Obtener Nutrientes. Obtener el Oxígeno del aire. Eliminar
carroñeros animal herbívoros cadáveres detritívoros animales omnívoros carnívoros hierba restos vegetal Las vacas comen. Son animales.
 6 Nutrición y reproducción de los animales PLAN DE MEJORA. Ficha 1 Los animales toman alimentos que proceden de otros seres vivos. Según su forma de alimentarse, pueden ser: carnívoros, herbívoros, omnívoros
6 Nutrición y reproducción de los animales PLAN DE MEJORA. Ficha 1 Los animales toman alimentos que proceden de otros seres vivos. Según su forma de alimentarse, pueden ser: carnívoros, herbívoros, omnívoros
TEMA 5 REINO ANIMAL I INVERTEBRADOS
 TEMA 5 REINO ANIMAL I INVERTEBRADOS ALUMNO/A CURSO: 1.- R e i n o Animal. Características del reino Animal: 1 Tienen las células eucariotas 2 Son pluricelulares. Es decir formados por la unión de muchas
TEMA 5 REINO ANIMAL I INVERTEBRADOS ALUMNO/A CURSO: 1.- R e i n o Animal. Características del reino Animal: 1 Tienen las células eucariotas 2 Son pluricelulares. Es decir formados por la unión de muchas
Los animales inverteblrados
 Los animales inverteblrados Indice: -Los poriferos -Los celentereos -Los platelmintos -Los nematodos -Los anelidos -Los moluscos -Gasteropodos -Los bilvalvos -Los cefalos -Los artropodos -Los insectos
Los animales inverteblrados Indice: -Los poriferos -Los celentereos -Los platelmintos -Los nematodos -Los anelidos -Los moluscos -Gasteropodos -Los bilvalvos -Los cefalos -Los artropodos -Los insectos
ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS Y VERTEBRADOS
 UNIDAD 13 14 ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS Y VERTEBRADOS ACTIVIDADES 1. Qué tipo de organismos son los equinodermos según su alimentación? a) Son organismos autótrofos que se alimentan a partir de algas unicelulares.
UNIDAD 13 14 ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS Y VERTEBRADOS ACTIVIDADES 1. Qué tipo de organismos son los equinodermos según su alimentación? a) Son organismos autótrofos que se alimentan a partir de algas unicelulares.
Identificación del material AICLE
 CONSEJERÍA DE EDUCACIÓN Dirección General de Participación e Innovación Educativa Identificación del material AICLE TÍTULO Animals NIVEL LINGÜÍSTICO SEGÚN MCER A1.3 IDIOMA Inglés ÁREA / MATERIA Conocimiento
CONSEJERÍA DE EDUCACIÓN Dirección General de Participación e Innovación Educativa Identificación del material AICLE TÍTULO Animals NIVEL LINGÜÍSTICO SEGÚN MCER A1.3 IDIOMA Inglés ÁREA / MATERIA Conocimiento
NOMBRE CÓDIGO CURSO FECHA FIRMA PADRE DE FAMILIA C.C. PECES AVES HOMBRE LOMBRIZ
 COLEGIO NICOLAS ESGUERRA ÁREA DE CIENCIAS NATURALES - TALLER DE AVANCES ACADÉMICOS COMO ACTIVIDAD COMPLEMENTARIA Y PROFUNDIZACIÓN (601-602-603-606) DOCENTE: ESTEFANÍA FORERO JIMÉNEZ NOMBRE CÓDIGO CURSO
COLEGIO NICOLAS ESGUERRA ÁREA DE CIENCIAS NATURALES - TALLER DE AVANCES ACADÉMICOS COMO ACTIVIDAD COMPLEMENTARIA Y PROFUNDIZACIÓN (601-602-603-606) DOCENTE: ESTEFANÍA FORERO JIMÉNEZ NOMBRE CÓDIGO CURSO
ESTUDIEMOS EL REINO ANIMAL
 ESTUDIEMOS EL REINO ANIMAL Las clases de Ciencia y Ambiente con la profesora Ana son emocionantes. El primer viernes de cada mes, ella realiza una actividad diferente con sus estudiantes. En esta ocasión
ESTUDIEMOS EL REINO ANIMAL Las clases de Ciencia y Ambiente con la profesora Ana son emocionantes. El primer viernes de cada mes, ella realiza una actividad diferente con sus estudiantes. En esta ocasión
Los seres vivos/ living things. CONOCIMIENTO DEL MEDIO 3º DE PRIMARIA
 CONOCIMIENTO DEL MEDIO 3º DE PRIMARIA Los contenidos de la asignatura Conocimiento del Medio se agrupan en tres bloques, uno por trimestre y constan de 5 unidades cada uno. Teniendo en cuenta la temporalización
CONOCIMIENTO DEL MEDIO 3º DE PRIMARIA Los contenidos de la asignatura Conocimiento del Medio se agrupan en tres bloques, uno por trimestre y constan de 5 unidades cada uno. Teniendo en cuenta la temporalización
Module 1: The classifica7on of living things. Natural Sciences 5
 Module 1: The classifica7on of living things Natural Sciences 5 The classifica7on of living things (La clasificación de los seres vivos). All living things can be classified according to their characteris7cs.
Module 1: The classifica7on of living things Natural Sciences 5 The classifica7on of living things (La clasificación de los seres vivos). All living things can be classified according to their characteris7cs.
CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS SERES VIVOS. 3º Ciclo de Primaria Curso 17/18 1 Colegio Virgen del Mar Tutor: Pepe Portillo
 CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS SERES VIVOS 3º Ciclo de Primaria Curso 17/18 1 Colegio Virgen del Mar Tutor: Pepe Portillo 3º Ciclo de Primaria Curso 17/18 2 Colegio Virgen del Mar Tutor: Pepe Portillo REINO FILO
CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS SERES VIVOS 3º Ciclo de Primaria Curso 17/18 1 Colegio Virgen del Mar Tutor: Pepe Portillo 3º Ciclo de Primaria Curso 17/18 2 Colegio Virgen del Mar Tutor: Pepe Portillo REINO FILO
Características del Reino Animal
 Características del Reino Animal Los animales son seres eucariotas, pluricelulares, heterótrofos, cuyas células no poseen pared y se agrupan formando tejidos. Generalmente, su reproducción es sexual. Los
Características del Reino Animal Los animales son seres eucariotas, pluricelulares, heterótrofos, cuyas células no poseen pared y se agrupan formando tejidos. Generalmente, su reproducción es sexual. Los
Los animales vertebrados poseen características que les permiten avanzar y flotar en el agua o sumergirse a distintas profundidades.
 Animales vertebrados Los animales vertebrados se dividen en 5 grandes grupos: los peces, los anfibios, los reptiles, las aves y los mamíferos. Estos animales han desarrollado, durante millones de años
Animales vertebrados Los animales vertebrados se dividen en 5 grandes grupos: los peces, los anfibios, los reptiles, las aves y los mamíferos. Estos animales han desarrollado, durante millones de años
7.1 Los animales invertebrados. 7.2 Los poríferos y cnidarios. Los poríferos. Cnidarios
 Tema 7 Los animales invertebrados 7.1 Los animales invertebrados Son el grupo de animales más numeroso y presentan gran variedad en sus características: Tamaño variado. Generalmente se desplazan pero también
Tema 7 Los animales invertebrados 7.1 Los animales invertebrados Son el grupo de animales más numeroso y presentan gran variedad en sus características: Tamaño variado. Generalmente se desplazan pero también
CORDADOS. Animales triblásticos, celomados y con simetría bilateral.
 CORDADOS CORDADOS Animales triblásticos, celomados y con simetría bilateral. Presentan en algún momento de su vida (a veces sólo en el embrión), los siguientes caracteres: - Cordón nervioso dorsal. - Notocorda
CORDADOS CORDADOS Animales triblásticos, celomados y con simetría bilateral. Presentan en algún momento de su vida (a veces sólo en el embrión), los siguientes caracteres: - Cordón nervioso dorsal. - Notocorda
ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS
 ACTIVIDAD 3 1º de ESO ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS NOTAS AL MARGEN SUBRAYADO ESQUEMAS RESUMEN Lee rápidamente el Texto Animales Vertebrados. Lee de forma detenida cada párrafo y escribe las NOTAS AL MARGEN. Teniendo
ACTIVIDAD 3 1º de ESO ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS NOTAS AL MARGEN SUBRAYADO ESQUEMAS RESUMEN Lee rápidamente el Texto Animales Vertebrados. Lee de forma detenida cada párrafo y escribe las NOTAS AL MARGEN. Teniendo
Tema 2: ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS
 Tema 2: ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS Los vertebrados Poseen esqueleto interno, destacando la columna vertebral Cabeza Cuerpo dividido en Tronco Cola (algunos no tienen. Ej.: ranas) Extremidades (algunos no tienen.
Tema 2: ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS Los vertebrados Poseen esqueleto interno, destacando la columna vertebral Cabeza Cuerpo dividido en Tronco Cola (algunos no tienen. Ej.: ranas) Extremidades (algunos no tienen.
El Reino Animal Los animales vertebrados
 El Reino Animal Los animales vertebrados Nov 4 10:28 AM SEGUNDO CICLO DE PRIMARIA LOS ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS 1 REINO MONERAS REINO PROTOCTISTAS LOS SERES VIVOS REINO ANIMAL REINO FUNGI REINO VEGETAL nov
El Reino Animal Los animales vertebrados Nov 4 10:28 AM SEGUNDO CICLO DE PRIMARIA LOS ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS 1 REINO MONERAS REINO PROTOCTISTAS LOS SERES VIVOS REINO ANIMAL REINO FUNGI REINO VEGETAL nov
NIVELACION DE BIOLOGÍA TERCER PERIODO Nombre: Grado: 11º Fecha: Lectura: CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS SERES VIVOS
 NIVELACION DE BIOLOGÍA TERCER PERIODO 2016 Nombre: Grado: 11º Fecha: Lectura: CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS SERES VIVOS Los seres vivos se clasifican de acuerdo a las características que presenten, la Taxonomía
NIVELACION DE BIOLOGÍA TERCER PERIODO 2016 Nombre: Grado: 11º Fecha: Lectura: CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS SERES VIVOS Los seres vivos se clasifican de acuerdo a las características que presenten, la Taxonomía
CONOCIMIENTO DEL MEDIO, TERCERO DE PRIMARIA TEMA 3 -LOS ANIMALES RECURSOS
 CONOCIMIENTO DEL MEDIO, TERCERO DE PRIMARIA TEMA 3 -LOS ANIMALES RECURSOS Diccionario online: www.wordreference.com Juego para clasificar vertebrados e invertebrados http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/asset/lsps07_int_animalclass/?u
CONOCIMIENTO DEL MEDIO, TERCERO DE PRIMARIA TEMA 3 -LOS ANIMALES RECURSOS Diccionario online: www.wordreference.com Juego para clasificar vertebrados e invertebrados http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/asset/lsps07_int_animalclass/?u
UNIVERSIDAD DE SAN CARLOS DE GUATEMALA -USAC- ESCUELA DE FORMACIÓN DE PROFESORES DE ENSEÑANZA MEDIA EFPEM-
 LABORATORIO No. REINO ANIMAL I. Introducción. Dentro de las características generales de los animales se encuentran las siguientes: son multicelulares, heterótrofos, reproducción sexual y asexual, sus
LABORATORIO No. REINO ANIMAL I. Introducción. Dentro de las características generales de los animales se encuentran las siguientes: son multicelulares, heterótrofos, reproducción sexual y asexual, sus
UNIDAD 3. LOS ANIMALES
 UNIDAD 3. LOS ANIMALES 1. LOS ANIMALES 2. LA CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS 2.1. LOS ARTRÓPODOS 2.2. LOS MOLUSCOS 2.3. OTROS GRUPOS DE INVERTEBRADOS 3. LA CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS
UNIDAD 3. LOS ANIMALES 1. LOS ANIMALES 2. LA CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS 2.1. LOS ARTRÓPODOS 2.2. LOS MOLUSCOS 2.3. OTROS GRUPOS DE INVERTEBRADOS 3. LA CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS
A= Lombriz tierra. Anélido. B= Almeja. Bivalvo. Molusco. C= Estrella mar. Equinodermo.
 Centro para la Innovación y Desarrollo la Educación a Distancia ACTIVIDADES DE ESO Nombre y apellidos del alumno: Curso: 1º ESO Quincena 10 Asignatura: CIENCIAS DE LA NATURALEZA Fecha: Profesor la asignatura:
Centro para la Innovación y Desarrollo la Educación a Distancia ACTIVIDADES DE ESO Nombre y apellidos del alumno: Curso: 1º ESO Quincena 10 Asignatura: CIENCIAS DE LA NATURALEZA Fecha: Profesor la asignatura:
TEMA 10 LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS
 TEMA 10 LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS CARACTERÍSTICAS GENERALES DE LOS ANIMALES - Son seres pluricelulares cuyas células son eucariotas. - Estas células se encuentran agrupadas formando verdaderos tejidos.
TEMA 10 LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS CARACTERÍSTICAS GENERALES DE LOS ANIMALES - Son seres pluricelulares cuyas células son eucariotas. - Estas células se encuentran agrupadas formando verdaderos tejidos.
TEMA 17: Clasificación de los seres vivos. CRA Sexma de La Sierra. 17. CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS SERES VIVOS.
 1 17. CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS SERES VIVOS. 2 1.- LOS SERES VIVOS. En la Tierra habita una gran cantidad de seres vivos. Qué son los seres vivos? A diferencia de los seres inertes, los seres vivos pueden llevar
1 17. CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS SERES VIVOS. 2 1.- LOS SERES VIVOS. En la Tierra habita una gran cantidad de seres vivos. Qué son los seres vivos? A diferencia de los seres inertes, los seres vivos pueden llevar
Los animales invertebrados
 Los animales invertebrados Las esponjas Son acuáticas y viven pegadas a las rocas. Tienen forma de saco y presentan poros por los que filtran el agua. Los equinodermos Las medusas Los gusanos Los moluscos
Los animales invertebrados Las esponjas Son acuáticas y viven pegadas a las rocas. Tienen forma de saco y presentan poros por los que filtran el agua. Los equinodermos Las medusas Los gusanos Los moluscos
TEMA 3 Los animales vertebrados
 TEMA 3 Los animales vertebrados Animales que tienen columna vertebral, que forma parte de un esqueleto interno o endoesqueleto. Su cuerpo está dividido en tres partes: cabeza, tronco y cola, aunque algunos
TEMA 3 Los animales vertebrados Animales que tienen columna vertebral, que forma parte de un esqueleto interno o endoesqueleto. Su cuerpo está dividido en tres partes: cabeza, tronco y cola, aunque algunos
Identificación del material AICLE
 CONSEJERÍA DE EDUCACIÓN Dirección General de Participación e Innovación Educativa Identificación del material AICLE TÍTULO I love animals NIVEL LINGÜÍSTICO SEGÚN MCER A1.2 IDIOMA Inglés ÁREA / MATERIA
CONSEJERÍA DE EDUCACIÓN Dirección General de Participación e Innovación Educativa Identificación del material AICLE TÍTULO I love animals NIVEL LINGÜÍSTICO SEGÚN MCER A1.2 IDIOMA Inglés ÁREA / MATERIA
CARACTERÍSTICAS GENERALES
 CARACTERÍSTICAS GENERALES Organización Celular: Eucariota y Pluricelular. Nutrición: Heterótrofa por ingestión: fagocitosis y pinocitosis. Metabolismo: Aerobio es decir consumen oxigeno. Reproducción.
CARACTERÍSTICAS GENERALES Organización Celular: Eucariota y Pluricelular. Nutrición: Heterótrofa por ingestión: fagocitosis y pinocitosis. Metabolismo: Aerobio es decir consumen oxigeno. Reproducción.
DIVERSIDAD Animales. MSc. Paola Solera Steller 2012-I
 DIVERSIDAD Animales MSc. Paola Solera Steller 2012-I REINO ANIMALIA Pluricelulares Heterótrofos Reproducción sexual (gametos) y asexual (fragmentación y partenogenesis) Móviles durante alguna etapa de
DIVERSIDAD Animales MSc. Paola Solera Steller 2012-I REINO ANIMALIA Pluricelulares Heterótrofos Reproducción sexual (gametos) y asexual (fragmentación y partenogenesis) Móviles durante alguna etapa de
LOS SERES VIVOS. Los seres vivos son los que tienen vida, como las personas, los animales y las plantas.
 LOS SERES VIVOS Los seres vivos: Los seres vivos son los que tienen vida, como las personas, los animales y las plantas. Los seres inertes son los que no tienen vida, como las rocas, el suelo o el aire.
LOS SERES VIVOS Los seres vivos: Los seres vivos son los que tienen vida, como las personas, los animales y las plantas. Los seres inertes son los que no tienen vida, como las rocas, el suelo o el aire.
Los siguientes estudiantes no alanzaron los logros mínimos en la asignatura de BIOLOGIA:
 Los siguientes estudiantes no alanzaron los logros mínimos en la asignatura de BIOLOGIA: MORENO PAEZ DIEGO STEVEN. RUBIANO OCHOA ANDRY JULIETH. TARAZONA NAVARRO ANDREY SANTIAGO. TORRES NAVARRO ELIECER
Los siguientes estudiantes no alanzaron los logros mínimos en la asignatura de BIOLOGIA: MORENO PAEZ DIEGO STEVEN. RUBIANO OCHOA ANDRY JULIETH. TARAZONA NAVARRO ANDREY SANTIAGO. TORRES NAVARRO ELIECER
SOLUCIONES DE LAS ACTIVIDADES DE EVALUACIÓN
 Evaluación inicial 1. Comprobar la correcta agrupación en los cuatro reinos: animales, plantas, hongos y organismos más sencillos o microorganismos. 2. a) El gorila es un mamífero que respira mediante
Evaluación inicial 1. Comprobar la correcta agrupación en los cuatro reinos: animales, plantas, hongos y organismos más sencillos o microorganismos. 2. a) El gorila es un mamífero que respira mediante
La Tierra, un planeta habitado Transparencias
 C A P Í T U L O 4 La Tierra, un planeta habitado Transparencias MAPA CONCEPTUAL La Tierra, un planeta habitado. Transparencia nº 1 MAPA CONCEPTUAL UN SER VIVO TIENE SU ORIGEN a partir de La Tierra, un
C A P Í T U L O 4 La Tierra, un planeta habitado Transparencias MAPA CONCEPTUAL La Tierra, un planeta habitado. Transparencia nº 1 MAPA CONCEPTUAL UN SER VIVO TIENE SU ORIGEN a partir de La Tierra, un
TEMA: REINO ANIMAL. Nombre y apellidos: 1.- Qué significa que los animales son pluricelulares? Y que son autótrofos?
 ATENCIÓN No realices las actividades directamente en este documento. Guarda primero el documento en tu PC (en la carpeta que habrás creado en tus documentos). Complétalo y cuando lo hayas terminado envíaselo
ATENCIÓN No realices las actividades directamente en este documento. Guarda primero el documento en tu PC (en la carpeta que habrás creado en tus documentos). Complétalo y cuando lo hayas terminado envíaselo
LOS ANIMALES. Copia y contesta en tu cuaderno estas preguntas:
 A continuación te vas a encontrar información sobre LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS basada en el tema que aparece en tu libro de texto. Lee las siguientes instrucciones para que puedas trabajar el tema: -Deberás
A continuación te vas a encontrar información sobre LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS basada en el tema que aparece en tu libro de texto. Lee las siguientes instrucciones para que puedas trabajar el tema: -Deberás
REPASO PARA VACACIONES DE NAVIDAD
 Página 1 de 14 REPASO PARA VACACIONES DE NAVIDAD Estimados padres: En primer lugar, hacerles llegar nuestra felicitación en estas fiestas y desearles unas Felices Navidades. Para estas semanas de vacaciones,
Página 1 de 14 REPASO PARA VACACIONES DE NAVIDAD Estimados padres: En primer lugar, hacerles llegar nuestra felicitación en estas fiestas y desearles unas Felices Navidades. Para estas semanas de vacaciones,
ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS: PORÍFEROS Y CELENTÉREOS
 PORÍFEROS Y CELENTÉREOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS: PORÍFEROS Y CELENTÉREOS Características comunes Organización muy sencilla Se asemejan a plantas Carecen de órganos y aparatos La mayoría viven fijos en el
PORÍFEROS Y CELENTÉREOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS: PORÍFEROS Y CELENTÉREOS Características comunes Organización muy sencilla Se asemejan a plantas Carecen de órganos y aparatos La mayoría viven fijos en el
ERIZO LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS-EQUINODERMOS. Anfioxo o pez lanceta. Ascidia AULA 360 1º ESO UNIDAD 12 CIENCIAS DE LA NATURALEZA
 LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS-EQUINODERMOS ERIZO http://www.educaplus.org/play-53-organizaci%c3%b3n-de-un-equinodermo.html Anfioxo o pez lanceta Ascidia LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS-EQUINODERMOS Estrella de
LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS-EQUINODERMOS ERIZO http://www.educaplus.org/play-53-organizaci%c3%b3n-de-un-equinodermo.html Anfioxo o pez lanceta Ascidia LOS ANIMALES INVERTEBRADOS-EQUINODERMOS Estrella de
UNIDAD 5. CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS SERES VIVOS
 UNIDAD 5. CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS SERES VIVOS CONTENIDOS (ESTÁNDARES DE APRENDIZAJE): - Identifica los grandes grupos taxonómicos de los seres vivos. - Reconoce los cinco reinos en los que agrupan los seres
UNIDAD 5. CLASIFICACIÓN DE LOS SERES VIVOS CONTENIDOS (ESTÁNDARES DE APRENDIZAJE): - Identifica los grandes grupos taxonómicos de los seres vivos. - Reconoce los cinco reinos en los que agrupan los seres
-Ciclo reproductivo con alternancia generaciones
 Plantas -Ciclo reproductivo con alternancia generaciones -eucariotas multicelulares + fotosíntesis, proceso que ocurre en sus cloroplastos con ayuda de alguna forma de clorofila. - algunas de ellas, secundariamente,
Plantas -Ciclo reproductivo con alternancia generaciones -eucariotas multicelulares + fotosíntesis, proceso que ocurre en sus cloroplastos con ayuda de alguna forma de clorofila. - algunas de ellas, secundariamente,
CUESTIONARIO 4 GRADO CIENCIAS NATURALES COLEGIO ROSARIO DE SANTO DOMINGO DOCENTE: YULIS FONTALVO MEJÍA
 CUESTIONARIO 4 GRADO CIENCIAS NATURALES COLEGIO ROSARIO DE SANTO DOMINGO DOCENTE: YULIS FONTALVO MEJÍA 1. Los siguientes son ejemplos de Protistas: a. Ameba y paramecio b. Cocodrilo y serpiente c. Moho
CUESTIONARIO 4 GRADO CIENCIAS NATURALES COLEGIO ROSARIO DE SANTO DOMINGO DOCENTE: YULIS FONTALVO MEJÍA 1. Los siguientes son ejemplos de Protistas: a. Ameba y paramecio b. Cocodrilo y serpiente c. Moho
UNI T 2: ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS
 UNI T 2: ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS 1.- La evolución animal Algunos científicos han encontrado en restos de dinosaurios alas y plumas, con ello han llegado a la conclusión de que las aves son los descendientes
UNI T 2: ANIMALES VERTEBRADOS 1.- La evolución animal Algunos científicos han encontrado en restos de dinosaurios alas y plumas, con ello han llegado a la conclusión de que las aves son los descendientes
UNIDAD DIDÁCTICA LOS ANIMALES 1º CICLO
 UNIDAD DIDÁCTICA LOS ANIMALES 1º CICLO C.P. POETA JUAN OCHOA - AVILÉS MUNDO ANIMAL Los animales son seres vivos. A lo largo de su vida se alimentan, crecen y se reproducen. DÓNDE VIVEN LOS ANIMALES? Algunos
UNIDAD DIDÁCTICA LOS ANIMALES 1º CICLO C.P. POETA JUAN OCHOA - AVILÉS MUNDO ANIMAL Los animales son seres vivos. A lo largo de su vida se alimentan, crecen y se reproducen. DÓNDE VIVEN LOS ANIMALES? Algunos
Principales grupos de seres vivos. Biología y Geología
 Principales grupos de seres vivos Biología y Geología La clasificación biológica Taxonomía Nomenclatura biológica La clasificación de los seres vivos Reino protoctistas Reino hongos Reino plantas Reino
Principales grupos de seres vivos Biología y Geología La clasificación biológica Taxonomía Nomenclatura biológica La clasificación de los seres vivos Reino protoctistas Reino hongos Reino plantas Reino
TEMA 4. Los animales vertebrados
 TEMA 4. Los animales vertebrados Los cordados y vertebrados Los cordados presentan en algún estadio de su ciclo vital una notocorda, un cordón nervioso, hendiduras branquiales y una cola. Los vertebrados
TEMA 4. Los animales vertebrados Los cordados y vertebrados Los cordados presentan en algún estadio de su ciclo vital una notocorda, un cordón nervioso, hendiduras branquiales y una cola. Los vertebrados
9/26/17. Invertebrados! Sebastián Padrón PhD!
 Invertebrados! Sebastián Padrón PhD! Carl Woese 1977-3 dominios.! Bacteria - Prokaryota! Archea - Prokaryota! Eucarya Eucariota Presencia de nucleo definido y organelos! Dominio Ekaryota! Reino Animalia
Invertebrados! Sebastián Padrón PhD! Carl Woese 1977-3 dominios.! Bacteria - Prokaryota! Archea - Prokaryota! Eucarya Eucariota Presencia de nucleo definido y organelos! Dominio Ekaryota! Reino Animalia
Los animales. Reino animales. Su clasificación. 1 TEMA 10: Los seres vivos CRA Sexma de La Sierra. CIENcias NAtuRAles. Alumno/a Aula Curso escolar
 1 TEMA 10: Los seres vivos CRA Sexma de La Sierra. CIENcias NAtuRAles Alumno/a Aula Curso escolar Los animales Reino animales Su clasificación Con células eucariotas (ADN en un núcleo) invertebrados vertebrados
1 TEMA 10: Los seres vivos CRA Sexma de La Sierra. CIENcias NAtuRAles Alumno/a Aula Curso escolar Los animales Reino animales Su clasificación Con células eucariotas (ADN en un núcleo) invertebrados vertebrados
TEMA 2.Los Animales invertebrados
 TEMA 2.Los Animales invertebrados El reino Animal Los animales son seres vivos con células eucariotas organizadas en tejidos y tienen nutrición heterótrofa. Los animales se clasifican según diversos criterios:
TEMA 2.Los Animales invertebrados El reino Animal Los animales son seres vivos con células eucariotas organizadas en tejidos y tienen nutrición heterótrofa. Los animales se clasifican según diversos criterios:
Ramón Ramírez Ruiz Ceip El Zargal Prog..AICLE 3º de primaria CONOCIMIENTO DEL MEDIO 3º DE PRIMARIA
 CONOCIMIENTO DEL MEDIO 3º DE PRIMARIA Los contenidos de la asignatura Conocimiento del Medio se agrupan en tres bloques, uno por trimestre y constan de 5 unidades cada uno. Teniendo en cuenta la temporalización
CONOCIMIENTO DEL MEDIO 3º DE PRIMARIA Los contenidos de la asignatura Conocimiento del Medio se agrupan en tres bloques, uno por trimestre y constan de 5 unidades cada uno. Teniendo en cuenta la temporalización
Todos los animales cambian y crecen. Las crías se vuelven adultos, qué les parece! Algunas hembras ponen huevos de los que las crías nacen.
 Poema del tema Todos los animales cambian y crecen. Las crías se vuelven adultos, qué les parece! Algunas hembras ponen huevos de los que las crías nacen. Aves, anfibios, reptiles y la mayoría de los peces
Poema del tema Todos los animales cambian y crecen. Las crías se vuelven adultos, qué les parece! Algunas hembras ponen huevos de los que las crías nacen. Aves, anfibios, reptiles y la mayoría de los peces
REFUERZO. 4 Fecha: 1 Completa esta tabla: 2 Escribe órganos o aparatos de los diferentes grupos de animales que se encarguen de:
 4 Fecha: Ciencias de la Naturaleza 5.º 1 Completa esta tabla: ANIMAL VETEBADO O INVETEBADO GUPO Lombriz de tierra Mejillón Elefante Anémona Cigüeña Delfín Sardina Lagarto Sapo Mosquito Erizo de mar 2 Escribe
4 Fecha: Ciencias de la Naturaleza 5.º 1 Completa esta tabla: ANIMAL VETEBADO O INVETEBADO GUPO Lombriz de tierra Mejillón Elefante Anémona Cigüeña Delfín Sardina Lagarto Sapo Mosquito Erizo de mar 2 Escribe
MINISTERIO DE EDUCACIÓN PLAN APOYO COMPARTIDO 3º BÁSICO CIENCIAS NATURALES 2012
 MINISTERIO DE EDUCACIÓN PLAN APOYO COMPARTIDO Material de Apoyo 3º BÁSICO CIENCIAS NATURALES 2012 Material de apoyo - Período 1 Ciencias Naturales - 3 básico MINISTERIO DE EDUCACIÓN PLAN APOYO COMPARTIDO
MINISTERIO DE EDUCACIÓN PLAN APOYO COMPARTIDO Material de Apoyo 3º BÁSICO CIENCIAS NATURALES 2012 Material de apoyo - Período 1 Ciencias Naturales - 3 básico MINISTERIO DE EDUCACIÓN PLAN APOYO COMPARTIDO
animal animal La Reproducción La Reproducción
 animal La Reproducción Palabras: 1,245 Imágenes: Shutterstock Fuente: http://definicion.de/viviparo/#ixzz2bh1v16mi http://deconceptos.com/ciencias-naturales/animales http://www.monografias.com http://www.educarchile.cl
animal La Reproducción Palabras: 1,245 Imágenes: Shutterstock Fuente: http://definicion.de/viviparo/#ixzz2bh1v16mi http://deconceptos.com/ciencias-naturales/animales http://www.monografias.com http://www.educarchile.cl
