SERIE BLANCA NORMAL Y PATOLÓGICA. Bqco. Gonzalo Ojeda Hematología Clínica Fa.C.E.N.A U.N.N.E 2011
|
|
|
- Vanesa Ortega Díaz
- hace 7 años
- Vistas:
Transcripción
1 SERIE BLANCA NORMAL Y PATOLÓGICA Bqco. Gonzalo Ojeda Hematología Clínica Fa.C.E.N.A U.N.N.E 2011
2 LEUCOPOYESIS
3
4 Leucocitos granulares Neutrófilos( 50-70%) Basófilos(0-2%) Eosinófilos (0-5%) Leucocitos agranulares Monocitos (1-9%) Linfocitos(20-40%)
5
6 CAYADOS SEGMENTADOS EOSINOFILOS BASOFILOS LINFOCITOS MONOCITOS RELATIVA % 0 a 3 50 a 70 1 a 4 0 a 1 20 a 40 2 a 8 ABSOLUTA (mm3) 0 a a a a a a 800
7 FUNCIONES DESTACADAS GRANULOCITOS : inmunidad innata MONOCITOS: inmunidad innata/adaptativa LINFOCITOS: inmunidad adaptativa
8 GRANULOCITOS
9 GRANULOPOYESIS NEUTRÓFILO
10 GRANULOPOYESIS EOSINÓFILO y BASÓFILOS
11 Célula Factores quimiotácticos y activadores Mediadores Neutrófilo IL-8, TNF-α, IL-1 Radicales libres de oxígeno, NO, prostaglandinas, leucotrienos, PAF, citoquinas Eosinófilos Monocitos Mastocitos, basófilos. IL-5,C5a, MIP-1 MCP-1, MIP 1. IL-8, MCP-1. Proteínas catiónicas, radicales libres de oxígeno, fosfolípidos, citoquinas Mediadores lipídicos, citoquinas. Histamina, mediadores lipídicos, citoquinas.
12 NEUTRÓFILO
13 NEUTRÓFILO
14 GRANULOCITO NEUTRÓFILO SP:3000 A 6000 cel/mm3 Tamaño: µm GRANULOS 1 - AZUROFILOS INESPECIFICOS Lisosomas 1,10 a 20% del contenido granular Mieloperoxidasa (MPO) Fosfatasa acida (FAC) Esterasas Beta glucuronidasa y beta galactosidasa Lisozima Otras proteinas básicas catiónicas
15 *VESICULAS SECRETORIAS: Contienen FAL *GRANULOS GELATINOSOS Gelatinasa, lisozima *Contienen alto contenido de glucógeno citoplasmático
16 *GRANULOS SECUNDARIOS O ESPECIFICOS Constituyen el 80-90% de los gránulos, son anfóteros se tiñen lila o rojizo *Fosfatasa acida (FAC) *Lactoferrina *Fagocitina *Proteínas catiónicas leucocitaria (pirógenos) * Lisozima *NADPH oxidasa *Proteína de unión de la B12
17 FUNCIONES DEL GN 1-Defensa antimicrobiana: fagocitosis, bactericidia 2-Síntesis de la Proteína transportadora de B12 3- Síntesis de pirógeno leucocitario 4-Biosíntesis de nucleótidos
18 MECANISMOS DE LA FUNCION FAGOCITARIA ADHERENCIA AL ENDOTELIO QUIMIOTAXIS OPSONIZACION Y RECONOCIMIENTO ENDOCITOSIS O INGESTION DEGRANULACION ACTIVACION DEL METABOLISMO OXIDATIVO SISTEMAS BACTERICIDAS
19
20
21 ALTERACIONES FUNCIONALES ADHERENCIA QUIMIOTAXIS GRÁNULOS ACTIVIDAD OXIDATIVA CD11/CD18 CITOESQUELETO Rc DE MEMB CHEDIAK H DEFICIT DE MPO EGC DEFICT DE G6PDH
22 MIELOBLASTOS Size of the cell: m Shape of the cell: oval, sometimes round Colour of cytoplasm: blue, without distinct perinuclear halo or with extended perinuclear halo Granularity: nongranular cytoplasm or a few thick azurophilic granules Nucleus' shape: usually oval, sometimes irregular, rarely round Type of chromatin: fine, with reticular appearance Nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio: high Nucleoli: visible, medium or large size 1 to 4; brighter than chromatin Occurrence: blood: not present marrow: < 5% Comment: One myeloblast and two more mature neutrophilic cells (myelocyte and band neutrophil leucocyte) are seen. Platelets with small number of granules. Staining: MGG Magnification: x myeloblast 2. neutrophil myelocyte 3. band neutrophil
23 MIELOBLASTOS Size of the cell: m Shape of the cell: oval, sometimes round Colour of cytoplasm: blue, without distinct perinuclear halo or with extended perinuclear halo Granularity: nongranular cytoplasm or a few thick azurophilic granules Nucleus' shape: usually oval, sometimes irregular, rarely round Type of chromatin: fine, with reticular appearance Nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio: high or relatively high Nucleoli: visible, medium or large size 1 to 4; brighter than chromatin Occurrence: blood: not present marrow: < 5% Comment: Early myeloblast with very high cytoplasm - nucleus ratio, without granules. In the picture there are numerous other cells representing next stages of maturation of the series of granulopoiesis. Staining: MGG Magnification: x myeloblast 2. promyelocyte 3. neutrophil myelocyte 4. neutrophil metamyelocyte 5. band neutrophil 6. segmented neutrophil 7. pycnotic normoblast 8. polychromatic normoblast 9. basophilic normoblast 10. proerythroblast
24 PROMIELOCITOS Size of the cell: m Shape of the cell: oval or round Colour of cytoplasm: light-blue, with distinct halo Granularity: thick, azurophilic abundant or very abundant Nucleus' shape: oval Type of chromatin: start of condensation Nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio: moderate, low or very low Nucleoli: visible, medium or large size, brighter than chromatin, 1-2. Sometimes not visible. Occurrence: blood: not present marrow: < 5 % Comment: The arrow indicates one promyelocyte, which is the only promyelocyte in the field. The nearby large cell of the granulopoiesis series is not a completely differentiated promyelocyte (lack of perinuclear zone, and not abundant granules). Staining: MGG Magnification: x neutrophil myelocyte 2. neutrophil metamyelocyte 3. band neutrophil 4. segmented neutrophil 5. plasmocyte 6. eosinophil 7. megakaryoblast
25 PROMIELOCITOS Size of the cell: m Shape of the cell: oval or round Colour of cytoplasm: light-blue, with distinct halo Granularity: thick, azurophilic abundant or very abundant Nucleus' shape: oval Type of chromatin: start of condensation Nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio: moderate, low or very low Nucleoli: visible, medium or large size, brighter than chromatin, 1-2. Sometimes not visible. Occurrence: blood: not present marrow: < 5 % Comment: The promyelocyte contains very abundant primary granules and a distinct zone of perinuclear halo. Degranulated platelets and discrete anisocytosis of the erythrocytes are also seen. Staining: MGG Magnification: 1000
26 PROMIELOCITOS Size of the cell: m Shape of the cell: oval or round Colour of cytoplasm: light-blue, with distinct halo Granularity: thick, azurophilic abundant or very abundant Nucleus' shape: oval Type of chromatin: start of condensation Nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio: moderate, low or very low Nucleoli: visible, medium or large size, brighter than chromatin, 1-2. Sometimes not visible. Occurrence: blood: not present marrow: < 5 % Comment: The promyelocyte contains abundant primary granules and a distinct zone of perinuclear halo. Also distinct anisocytosis of the erythrocytes. Staining: MGG Magnification: x 1000
27 Size of the cell: m Shape of the cell: oval or round Colour of cytoplasm: light-blue or of pale pink colour undiscernible halo Granularity: abundant, thick azurophilic and neutrophilic granulation Nucleus' shape: oval or kidney shaped Type of chromatin: partially condensed Nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio: low or very low Nucleoli: not visible MIELOCITOS NEUTRÓFILOS Occurrence: blood: not present marrow: 5-20 % Comment: The arrow indicates neutrophil myelocyte with pink cytoplasm and disappearing primary granules. In the field there are also four other cells at a similar stage of maturation and numerous other maturating neutrophil cells. Staining: MGG Magnification: x neutrophil myelocyte 2. neutrophil metamyelocyte 3. band neutrophil 4. segmented neutrophil 5. lymphocyte 6. plasmocyte 7. proerythroblast 8. polychromatic normoblast 9. pycnotic normoblast
28 Size of the cell: m MIELOCITOS NEUTRÓFILOS Shape of the cell: oval or round Colour of cytoplasm: light-blue or of pale pink colour undiscernible halo Granularity: abundant, thick azurophilic and neutrophilic granulation Nucleus' shape: oval or kidney shaped Type of chromatin: partially condensed Nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio: low or very low Nucleoli: not visible Occurrence: blood: not present marrow: 5-20 % Comment: Early neutrophil myelocyte in the blood. Also two matured neutrophilic leucocytes, a lymphocyte and platelets. Staining: MGG Magnification: x 1000
29 METAMIELOCITOS NEUTRÓFILOS Size of the cell: m Shape of the cell: oval or round Colour of cytoplasm: pink Granularity: a few azurophilic and neutrophilic, different in number Nucleus' shape: elongated, semicircular Type of chromatin: condensed Nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio: low or very low Nucleoli: not visible Occurrence: blood: not present marrow: % Comment: The arrow indicates a neutrophil metamyelocyte, one of seven present in the picture. Also other forms of maturating granulopoiesis are seen. Staining: MGG Magnification: x neutrophil metamyelocyte 2. neutrophil myelocyte 3. promonocyte 4. promyelocyte 5. plasmocyte 6. basophilic normoblast 7. polychromatic normoblast 8. pycnotic normoblast
30 METAMIELOCITOS NEUTRÓFILOS Size of the cell: m Shape of the cell: oval or round Colour of cytoplasm: pink Granularity: a few azurophilic and neutrophilic, different in number Nucleus' shape: elongated, semicircular Type of chromatin: condensed Nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio: low or very low Nucleoli: not visible Occurrence: blood: not present marrow: % Comment: Neutrophil metamyelocyte indicated by the arrow is present in blood. Besides, neutrophil segmented and band-forms leucocytes are seen. Platelets not rich in granules. Staining: MGG Magnification: x 1000
31 Size of the cell: m Shape of the cell: oval or round CAYADOS Colour of cytoplasm: pink Granularity: a few azurophilic and neutrophilic, different in number Nucleus' shape: semicircular Type of chromatin: condensed Nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio: low or very low Nucleoli: not visible Occurrence: blood: < 5% marrow: 5-20 % Comment: Two band forms and one segmented neutrophil leucocytes in the blood. Also crenated blood cells and platelets without granules are seen. Staining: MGG Magnification: x 1000
32 CRITERIOS PARA CLASIFICAR UN NEUTRÓFILO COMO EN CAYADO -CUANDO NO SE OBSERVA LOBULACIÓN EVIDENTE -CUANDO EL NÚCLEO TIENE DIÁMETRO UNIFORME SIN ESTRANGULACIÓN EVIDENTE -SI EL NÚCLEO PRESENTA UNA PARTE MÁS DELGADA, ESTA NO DEBE SER MENOR A 1/3 DE LA PARTE DE MAYOR GROSOR
33
34
35 Size of the cell: m Shape of the cell: oval or round NEUTRÓFILO SEGMENTADO Colour of cytoplasm: pink Granularity: a few azurophilic and neutrophilic, different in number granulation Nucleus' shape: lobulated (normally less than 5 lobes) Type of chromatin: condensed Nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio: low or very low Nucleoli: not visible Occurrence: blood: % marrow: 5-20 % Comment: Three-lobulated segmented neutrophil leucocyte with fine neutrophil granularity. Staining: MGG Magnification: x 1000
36
37 ALTERACIONES LEUCOCITARIAS CUANTITATIVAS CUALITATIVAS F(X) LEUCOPENIAS LEUCOCITOSIS NUCLEARES CITOPLASMÁTICAS
38 NUCLEARES OTROS HIPOSEG HIPERSEG CONGENITA ADQUIRIDA CONGÉNITA ADQUIRIDA PELGER HÜET PSEUDO PELGER O PELGUEROIDE UNDRITZ DÉFICIT DE B12 SMD SMD EMBARAZADAS FARMACOS SEPSIS DE MALA EV LMA-LMC
39 CITOPLASMÁTICAS CONGÉNITAS ADQUIRIDAS -A. DE CHEDIAK-HIGASHI -A. DE MAY HEGGLIN -A. DE ALDER -DEGRANULADOS -GRAN. TÓXICAS -VACUOLAS -CUERPOS DE DöHLE -DEGRANULADOS
40 HIPOSEGMENTACIÓN NUCLEAR NO CONFUNDIR PELGER CON CAYADOS CROMATINA MEDIANAMENTE CONDENSADA CROMATINA HIPERCON- DENSADA LLEGA A MADURO SIN SEGMENTAR
41 PELGER HÜET AUTOSÓMICO DOMINATE PUEDE SER HOMO O HETEROCIGOTA PUEDE AFECTAR TB A EOS Y BASOFILOS HOMOCIGOTA HETEROCIGOTA STODSMEYSTER
42
43 HIPERSEGMENTACIÓN > A 5 LÓBULOS LIGERO AUMENTO DE TAMAÑO CELULAR CONGÉNITA (UNDRITZ) AUTOSÓMICA DOMINANTE- MUY RARA-80 A 90 % NEUTRÓFILOS CON MÁS DE 5 LÓBULOS PUEDE AFECTAR A EOSINÓFILOS ADQUIRIDA- BASTANTE FRECUENTE- SMD-ANEMIAS MEGALOBLÁSTICAS - ALCOHOLISMO
44 HIPERSEGMENTANCIÓN
45 HIPERSEGMENTANCIÓN
46 ALTERACIONES CITOPLASMÁTICAS CHEDIAK HIGASHI
47
48
49 ALBINISMO PARCIAL
50 MAY HEGGLIN
51
52
53 ALDER REILLY
54
55 NEUTROFILO AGRANULAR Occurrence in blood: normally not present Comment: Granulesless segmented neutrophil. Staining: MGG Magnification: x 1000
56 GRANULACIONES TOXICAS Granularity: thick granules, more eosinophilic stained than typical neutrophilic granularity. Single granules with a tendency to aggregate. Occurrence in blood: normally not present Comment: Band neutrophil leucocyte with dark, very abundant toxic granulation. Also anisocytosis of erythrocytes. Numerous ovalocytes. Normal platelets. Staining: MGG Magnification: x 1000
57
58 CUERPOS DE DÖHLE Definition: Dotted inclusions of blue, non-granular cytoplasm in pink cytoplasm of mature neutrophil leucocyte. Occurrence in blood: normally not present. Comment: The arrow points Döhle s body in the granulocyte. Erythrocytes difficult to assess. Staining: MGG Magnification: x 1000
59 Definition: Dotted inclusions of blue, nongranular cytoplasm in pink cytoplasm of mature neutrophil leucocyte. Occurrence in blood: normally not present. Comment: Döhle s body pointed by the arrow. Also anisocytosis of erythrocytes. Staining: MGG Magnification: x 1000
60 VACUOLAS Occurrence: normal mature neutrophil leucocytes may contain single small vacuoles in cytoplasm Comment: Distinct vacuoles changes in the neutrophilic leucocytes. Two target cells and one ovalocyte are present. Staining: MGG Magnification: x 1000
61 VACUOLAS Occurrence: normal mature neutrophil leucocytes may contain single small vacuoles in cytoplasm Comment: Small vacuoles in a neutrophil leucocyte with fine neutrophilic granulation. Also anizocytosis of erythrocytes. A single spherocyte and a polychromatophilic cell are seen. Staining: MGG Magnification: x 1000
62
63 NEUTRÓFILO APOPTÓTICO/MUESTRA VIEJA
SERIE BLANCA NORMAL Y PATOLÓGICA. Bqco. Gonzalo Ojeda Hematología Clínica Fa.C.E.N.A U.N.N.E 2013
 SERIE BLANCA NORMAL Y PATOLÓGICA Bqco. Gonzalo Ojeda Hematología Clínica Fa.C.E.N.A U.N.N.E 2013 LEUCOPOYESIS NUEVOS MODELOS Leucocitos granulares Neutrófilos( 50-70%) Basófilos(0-2%) Eosinófilos (0-5%)
SERIE BLANCA NORMAL Y PATOLÓGICA Bqco. Gonzalo Ojeda Hematología Clínica Fa.C.E.N.A U.N.N.E 2013 LEUCOPOYESIS NUEVOS MODELOS Leucocitos granulares Neutrófilos( 50-70%) Basófilos(0-2%) Eosinófilos (0-5%)
LEUCOCITOS *GRANULOCITOS O POLIMORFONUCLEARES: *MONONUCLEADOS Linfocitos,monocitos
 LEUCOCITOS *GRANULOCITOS O POLIMORFONUCLEARES: Neutrófilos, eosinófilos, basófilos *MONONUCLEADOS Linfocitos,monocitos GRANULOCITO NEUTROFILO *SP:4000-42504250 cel/mm3 *Tamaño: 12-13um 13um *GRANULOS 1ª,AZUROFILOS
LEUCOCITOS *GRANULOCITOS O POLIMORFONUCLEARES: Neutrófilos, eosinófilos, basófilos *MONONUCLEADOS Linfocitos,monocitos GRANULOCITO NEUTROFILO *SP:4000-42504250 cel/mm3 *Tamaño: 12-13um 13um *GRANULOS 1ª,AZUROFILOS
GRANULOCITOS GRANULOPOYESIS Y FUNCIONALISMO LEUCOCITARIO. Abril 2012 Cátedra de Hematología Residente Dra. Jennifer Sauer
 GRANULOCITOS GRANULOPOYESIS Y FUNCIONALISMO LEUCOCITARIO Abril 2012 Cátedra de Hematología Residente Dra. Jennifer Sauer 60-65% de la celularidad medular Distribución topográfica constante Progenitores
GRANULOCITOS GRANULOPOYESIS Y FUNCIONALISMO LEUCOCITARIO Abril 2012 Cátedra de Hematología Residente Dra. Jennifer Sauer 60-65% de la celularidad medular Distribución topográfica constante Progenitores
PROMIELOCITO INICIAL:
 27 LEUCOPOYESIS ESTRUCTURA DEL TEMA: 27.1. Granulopoyesis. 27.2. Monopoyesis. 27.3. Linfopoyesis. 27.1. GRANULOPOYESIS Es el proceso de formación de los granulocitos (neutrófilos, eosinófilos y basófilos).
27 LEUCOPOYESIS ESTRUCTURA DEL TEMA: 27.1. Granulopoyesis. 27.2. Monopoyesis. 27.3. Linfopoyesis. 27.1. GRANULOPOYESIS Es el proceso de formación de los granulocitos (neutrófilos, eosinófilos y basófilos).
LEUCOPOYESIS Regulación ESTRUCTURA, PROPIEDADES Y FUNCIONES DE LOS LEUCOCITOS. Fórmula leucocitaria Absoluta/Relativa. Valores de referencia.
 LEUCOPOYESIS Regulación. ESTRUCTURA, PROPIEDADES Y FUNCIONES DE LOS LEUCOCITOS. Fórmula leucocitaria Absoluta/Relativa. Valores de referencia. Objetivos - Diferenciar Mielopoyesis de Linfopoyesis - Conocer
LEUCOPOYESIS Regulación. ESTRUCTURA, PROPIEDADES Y FUNCIONES DE LOS LEUCOCITOS. Fórmula leucocitaria Absoluta/Relativa. Valores de referencia. Objetivos - Diferenciar Mielopoyesis de Linfopoyesis - Conocer
HEMOGRAMA Recuento de GR Recuento de Leucocitos Hemoglobina Hematocrito Índices Hematimétricos Fórmula Leucocitaria Recuento de plaquetas
 HEMOGRAMA - Recuento de GR - Recuento de Leucocitos - Hemoglobina - Hematocrito - Índices Hematimétricos - Fórmula Leucocitaria - Recuento de plaquetas LEUCOCITOS Neutrófilo LEUCOCITOS EDAD
HEMOGRAMA - Recuento de GR - Recuento de Leucocitos - Hemoglobina - Hematocrito - Índices Hematimétricos - Fórmula Leucocitaria - Recuento de plaquetas LEUCOCITOS Neutrófilo LEUCOCITOS EDAD
Fagocitosis FAGOCITOSIS. Marcelo Castillo Navarrete, TM MsC (c) Facultad de Medicina Dpto. Especialidades Médicas Carrera Tecnología Médica
 Fagocitosis Marcelo Castillo Navarrete, TM MsC (c) Facultad de Medicina Dpto. Especialidades Médicas Carrera Tecnología Médica 09 de Marzo de 2006 SISTEMA INMUNE INMUNIDAD INNATA INFLAMACION INMUNIDAD
Fagocitosis Marcelo Castillo Navarrete, TM MsC (c) Facultad de Medicina Dpto. Especialidades Médicas Carrera Tecnología Médica 09 de Marzo de 2006 SISTEMA INMUNE INMUNIDAD INNATA INFLAMACION INMUNIDAD
LEUCOCITOS. neutrófilos eosinófilos basófilos. linfocitos células plasmáticas monocitos macrófagos tisulares GRANULOCITOS AGRANULOCITOS
 LEUCOCITOS GRANULOCITOS neutrófilos eosinófilos basófilos AGRANULOCITOS linfocitos células plasmáticas monocitos macrófagos tisulares LEUCOPOYESIS GRANULOPOYESIS CBH CPG granulopoyetina GM-CSF G-CSF EO-CSF
LEUCOCITOS GRANULOCITOS neutrófilos eosinófilos basófilos AGRANULOCITOS linfocitos células plasmáticas monocitos macrófagos tisulares LEUCOPOYESIS GRANULOPOYESIS CBH CPG granulopoyetina GM-CSF G-CSF EO-CSF
La fórmula leucocitaria, junto con los recuentos celulares siguen siendo pruebas de gran importancia biodiagnóstica.
 SERVICIO DE LABORATORIO 29 DE 7 7 LEUCOGRAMA 7.1 GENERALIDADES La fórmula leucocitaria, junto con los recuentos celulares siguen siendo pruebas de gran importancia biodiagnóstica. 7.2 OBJETIVO Con ella
SERVICIO DE LABORATORIO 29 DE 7 7 LEUCOGRAMA 7.1 GENERALIDADES La fórmula leucocitaria, junto con los recuentos celulares siguen siendo pruebas de gran importancia biodiagnóstica. 7.2 OBJETIVO Con ella
Universidad Mariano Gálvez Facultad de Ciencias Médicas y de la Salud Carrera de Médico y Cirujano CÉLULAS SANGUÍNEAS. Práctica 3
 CÉLULAS SANGUÍNEAS Práctica 3 1. Introducción La fórmula leucocitaria tiene por objetivo determinar los porcentajes de las distintas clases de leucocitos normales y anormales en la sangre. A partir de
CÉLULAS SANGUÍNEAS Práctica 3 1. Introducción La fórmula leucocitaria tiene por objetivo determinar los porcentajes de las distintas clases de leucocitos normales y anormales en la sangre. A partir de
Células del Sistema Inmune. Células y Órganos del Sistema Inmune
 Células y Órganos del Sistema Inmune Células del Sistema Inmune Marcelo Castillo Navarrete, TM MsC (c) Facultad de Medicina Dpto. Especialidades Médicas Carrera Tecnología Médica 08 de Marzo de 2006 HEMATOPOIESIS
Células y Órganos del Sistema Inmune Células del Sistema Inmune Marcelo Castillo Navarrete, TM MsC (c) Facultad de Medicina Dpto. Especialidades Médicas Carrera Tecnología Médica 08 de Marzo de 2006 HEMATOPOIESIS
Tema 5: Tejido Conectivo Especializado Sangre y Hematopoyesis Unidad de Histología
 Universidad la República Escuela de Salud Licenciatura en Enfermería Asignatura: Histología Tema 5: Tejido Conectivo Especializado Sangre y Hematopoyesis Unidad de Histología Mg Bárbara Cuevas Montuschi
Universidad la República Escuela de Salud Licenciatura en Enfermería Asignatura: Histología Tema 5: Tejido Conectivo Especializado Sangre y Hematopoyesis Unidad de Histología Mg Bárbara Cuevas Montuschi
LOS LEUCOCITOS LOS LEUCOCITOS II
 TEMA 5 LOS LEUCOCITOS LOS LEUCOCITOS I 1. INTRODUCCIÓN 2. CLASIFICACIÓN Y VALORES DE REFERENCIA 3. GRANULOCITOS 3.1 GRANULOPOYESIS 3.2 NEUTRÓFILO ESTRUCTURA FUNCIÓN. FAGOCITOSIS. INFLAMACIÓN AGUDA 3.3
TEMA 5 LOS LEUCOCITOS LOS LEUCOCITOS I 1. INTRODUCCIÓN 2. CLASIFICACIÓN Y VALORES DE REFERENCIA 3. GRANULOCITOS 3.1 GRANULOPOYESIS 3.2 NEUTRÓFILO ESTRUCTURA FUNCIÓN. FAGOCITOSIS. INFLAMACIÓN AGUDA 3.3
ANOMALÍAS MORFOLÓGICAS DE LOS LEUCOCITOS EN EL NIÑO ASPECTO EN EL FROTIS
 ANOMALÍAS MORFOLÓGICAS DE LOS LEUCOCITOS EN EL NIÑO ASPECTO EN EL FROTIS 69 Figura 1. En el curso de las infecciones bacterianas severas, cualquiera que sea la edad, los polinucleares neutrófilos presentan
ANOMALÍAS MORFOLÓGICAS DE LOS LEUCOCITOS EN EL NIÑO ASPECTO EN EL FROTIS 69 Figura 1. En el curso de las infecciones bacterianas severas, cualquiera que sea la edad, los polinucleares neutrófilos presentan
El proceso de fagocitosis comprende varios pasos secuenciales: quimiotaxis, adherencia de las partículas antigénicas a la superficie de los
 El proceso de fagocitosis comprende varios pasos secuenciales: quimiotaxis, adherencia de las partículas antigénicas a la superficie de los fagocitos, captación / ingestión (fagocitosis) y muerte intracelular
El proceso de fagocitosis comprende varios pasos secuenciales: quimiotaxis, adherencia de las partículas antigénicas a la superficie de los fagocitos, captación / ingestión (fagocitosis) y muerte intracelular
LEUCOCITOS SANGUÍNEOS
 UNIVERSIDAD CENTROCCIDENTAL LISANDRO ALVARADO DECANATO DE CIENCIAS DE LA SALUD DEPARTAMENTO DE CIENCIAS FUNCIONALES LEUCOCITOS SANGUÍNEOS Lic. Ana López-Fonseca ana.lopez@.ucla.edu.ve CONTENIDO Leucocitos
UNIVERSIDAD CENTROCCIDENTAL LISANDRO ALVARADO DECANATO DE CIENCIAS DE LA SALUD DEPARTAMENTO DE CIENCIAS FUNCIONALES LEUCOCITOS SANGUÍNEOS Lic. Ana López-Fonseca ana.lopez@.ucla.edu.ve CONTENIDO Leucocitos
Son denominados así por que carecen de color (leuco) por oposición a los eritrocitos que están coloreados por la Hemoglobina. Son células nucleadas
 HEMATOLOGIA 2014 Son denominados así por que carecen de color (leuco) por oposición a los eritrocitos que están coloreados por la Hemoglobina. Son células nucleadas de forma redondeada HEMATOLOGIA 2014
HEMATOLOGIA 2014 Son denominados así por que carecen de color (leuco) por oposición a los eritrocitos que están coloreados por la Hemoglobina. Son células nucleadas de forma redondeada HEMATOLOGIA 2014
ATLAS de HISTOLOGÍA VEGETAL y ANIMAL HISTOLOGÍA ANIMAL 3. TEJIDO CONJUNTIVO SANGRE
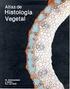 ATLAS de HISTOLOGÍA VEGETAL y ANIMAL HISTOLOGÍA ANIMAL 3. TEJIDO CONJUNTIVO SANGRE Pilar Molist Manuel A. Pombal Manuel Megías Depto. de Biología Funcional y Ciencias de la Salud Facultad de Biología Universidad
ATLAS de HISTOLOGÍA VEGETAL y ANIMAL HISTOLOGÍA ANIMAL 3. TEJIDO CONJUNTIVO SANGRE Pilar Molist Manuel A. Pombal Manuel Megías Depto. de Biología Funcional y Ciencias de la Salud Facultad de Biología Universidad
Tema 2.- Bases morfológicas del Sistema Inmunológico. Células, tejidos y órganos linfoides
 Tema 2.- Bases morfológicas del Sistema Inmunológico. Células, tejidos y órganos linfoides 1.- Células presentadoras de antígenos: Capturan y exponen los antígenos 2.- Células específicas: Reconocen y
Tema 2.- Bases morfológicas del Sistema Inmunológico. Células, tejidos y órganos linfoides 1.- Células presentadoras de antígenos: Capturan y exponen los antígenos 2.- Células específicas: Reconocen y
Inflamación (2) Exudación celular Quimiotaxis y Fagocitosis Defectos en la función leucocitaria
 Inflamación (2) Exudación celular Quimiotaxis y Fagocitosis Defectos en la función leucocitaria En los campos de la observación la suerte solo favorece a las mentes preparadas (L. Pasteur) Premisas Los
Inflamación (2) Exudación celular Quimiotaxis y Fagocitosis Defectos en la función leucocitaria En los campos de la observación la suerte solo favorece a las mentes preparadas (L. Pasteur) Premisas Los
Biología Celular y Sistémica 2011 Teórico : Citoplasma Dr. Roberto Najle
 Biología Celular y Sistémica 2011 Teórico : Citoplasma Dr. Roberto Najle Las dos formas de celulas Todas las células comparten ciertas características: -Todos ellos están cerrados por una membrana. -Todos
Biología Celular y Sistémica 2011 Teórico : Citoplasma Dr. Roberto Najle Las dos formas de celulas Todas las células comparten ciertas características: -Todos ellos están cerrados por una membrana. -Todos
ATLAS de HISTOLOGÍA VEGETAL y ANIMAL. Ti pos celulares. Manuel Megías, Pilar Molist, Manuel A. Pombal
 ATLAS de HISTOLOGÍA VEGETAL y ANIMAL Ti pos celulares EOSINÓFILO Manuel Megías, Pilar Molist, Manuel A. Pombal Departamento de Biología Funcional y Ciencias de la Salud. Facultad de Biología. Universidad
ATLAS de HISTOLOGÍA VEGETAL y ANIMAL Ti pos celulares EOSINÓFILO Manuel Megías, Pilar Molist, Manuel A. Pombal Departamento de Biología Funcional y Ciencias de la Salud. Facultad de Biología. Universidad
Atlas de Histología Animal y Vegetal Manuel Megías, Pilar Molist, Manuel A. Pombal
 Atlas de Histología Animal y Vegetal Conectivo SANGRE Manuel Megías, Pilar Molist, Manuel A. Pombal DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA FUNCIONAL Y CIENCIAS DE LA SALUD. FACULTAD DE BIOLOGÍA. UNIVERSIDAD DE VIGO.
Atlas de Histología Animal y Vegetal Conectivo SANGRE Manuel Megías, Pilar Molist, Manuel A. Pombal DEPARTAMENTO DE BIOLOGÍA FUNCIONAL Y CIENCIAS DE LA SALUD. FACULTAD DE BIOLOGÍA. UNIVERSIDAD DE VIGO.
I CURSO DE DIAGNÓSTICO INTEGRAL EN HEMATOLOGÍA. Módulo 4
 I CURSO DE DIAGNÓSTICO INTEGRAL EN HEMATOLOGÍA. Módulo 4 Dr. Joaquín Carrillo Farga Instituto de Hematopatología de México. Queretaro, México Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal Salón de Actos 3 y 4 de
I CURSO DE DIAGNÓSTICO INTEGRAL EN HEMATOLOGÍA. Módulo 4 Dr. Joaquín Carrillo Farga Instituto de Hematopatología de México. Queretaro, México Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal Salón de Actos 3 y 4 de
Sumario. El sistema Inmune Innato Componentes del Sistema. El Sistema Inmune Adquirido Componentes del Sistema. Colaboración entre ambos Sistemas
 Sumario El sistema Inmune Innato Componentes del Sistema El Sistema Inmune Adquirido Componentes del Sistema Colaboración entre ambos Sistemas El Sistema Inmune es el encargado de eliminar a los patógenos
Sumario El sistema Inmune Innato Componentes del Sistema El Sistema Inmune Adquirido Componentes del Sistema Colaboración entre ambos Sistemas El Sistema Inmune es el encargado de eliminar a los patógenos
Gonzalo A. Ojeda (Bioquímico- Doctor en Química, UNNE. Docente de la carrera de Bioquímica de la FACENA, UNNE)
 CURSO DE POSGRADO: Alteraciones No Neoplásicas de los Leucocitos Modalidad Virtual - Aprobado por Resolución Nº 559/16 CD Unidad Académica Responsable Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales y Agrimensura
CURSO DE POSGRADO: Alteraciones No Neoplásicas de los Leucocitos Modalidad Virtual - Aprobado por Resolución Nº 559/16 CD Unidad Académica Responsable Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales y Agrimensura
REPORTE DE CELULAS SANGUINEAS Y ANORMALIDADES ENCONTRADAS EN EL FSP. Jeanette Jurado Blanco Paola Andrea Acuña Bacteriologas, Dinamica Sede Palermo
 REPORTE DE CELULAS SANGUINEAS Y ANORMALIDADES ENCONTRADAS EN EL FSP Jeanette Jurado Blanco Paola Andrea Acuña Bacteriologas, Dinamica Sede Palermo GLOBULOS ROJOS ANTES: Normociticos Normocromicos (Clasificacion
REPORTE DE CELULAS SANGUINEAS Y ANORMALIDADES ENCONTRADAS EN EL FSP Jeanette Jurado Blanco Paola Andrea Acuña Bacteriologas, Dinamica Sede Palermo GLOBULOS ROJOS ANTES: Normociticos Normocromicos (Clasificacion
Sistemas de defensa activos INMUNIDAD INNATA. Inespecífica de antígeno
 Sistemas de defensa activos INMUNIDAD INNATA Inespecífica de antígeno Clasificación de los sistemas defensivos SISTEMAS PASIVOS (Barreras Físicas) PIEL MUCOSAS Digestiva Respiratoria Genitourinaria Ocular
Sistemas de defensa activos INMUNIDAD INNATA Inespecífica de antígeno Clasificación de los sistemas defensivos SISTEMAS PASIVOS (Barreras Físicas) PIEL MUCOSAS Digestiva Respiratoria Genitourinaria Ocular
José Carlos Giraldo T. MD Esp. Medicina Deportiva Mg en Fisiología. Carlos Eduardo Nieto G. MD Esp. Medicina Deportiva Esp: Salud Ocupacional
 José Carlos Giraldo T. MD Esp. Medicina Deportiva Mg en Fisiología Carlos Eduardo Nieto G. MD Esp. Medicina Deportiva Esp: Salud Ocupacional Los leucocitos (células sanguíneas de la serie blanca) incluyen
José Carlos Giraldo T. MD Esp. Medicina Deportiva Mg en Fisiología Carlos Eduardo Nieto G. MD Esp. Medicina Deportiva Esp: Salud Ocupacional Los leucocitos (células sanguíneas de la serie blanca) incluyen
Granulocitos - Neutrófilos: 60-65% del total de leucocitos. en situaciones de estrés. - Eosinófilos (1-3%) - Basófilos (0-1%)
 Marlen Arias Leucocitos (células sanguíneas de la serie blanca) incluye un grupo heterogéneo de poblaciones celulares derivadas de precursores hematopoyéticos que median la respuesta inmunológica del organismo.
Marlen Arias Leucocitos (células sanguíneas de la serie blanca) incluye un grupo heterogéneo de poblaciones celulares derivadas de precursores hematopoyéticos que median la respuesta inmunológica del organismo.
Los Leucocitos 10/10/2016. Recuento. Formula Leucocitaria. GRANULOCITOS, POLIMORFONUCLEARES ó POLINUCLEARES (PMN ó PN) ó SEGMENTADOS
 LEUCOCITOS Los Leucocitos Recuento. Formula Leucocitaria. Los leucocitos son células nucleadas, cuyo número oscila entre 4.000 y 11.000 por microlitro(μl) de sangre (4-11 x 10 3 /mm 3 ó μl) (si< Leucopenia,
LEUCOCITOS Los Leucocitos Recuento. Formula Leucocitaria. Los leucocitos son células nucleadas, cuyo número oscila entre 4.000 y 11.000 por microlitro(μl) de sangre (4-11 x 10 3 /mm 3 ó μl) (si< Leucopenia,
DÉBORA E. ALDANA SALGUERO, MD, PHD
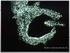 DÉBORA E. ALDANA SALGUERO, MD, PHD La palabra viene del griego: Phagos el que come Kytos, célula Metchnikoff (1880), descubrió que la función de las células fagocíticas era esencial para la supervivencia
DÉBORA E. ALDANA SALGUERO, MD, PHD La palabra viene del griego: Phagos el que come Kytos, célula Metchnikoff (1880), descubrió que la función de las células fagocíticas era esencial para la supervivencia
UNIVERSIDAD DE LA REPUBLICA. FACULTAD DE MEDICINA CICLO DE ESTRUCTURAS Y FUNCIONES NORMALES UTI "BIOLOGIA TISULAR" ENTREGA MODULO III FORMULARIO A
 UNIVERSIDAD DE LA REPUBLICA. FACULTAD DE MEDICINA CICLO DE ESTRUCTURAS Y FUNCIONES NORMALES UTI "BIOLOGIA TISULAR" ENTREGA MODULO III FORMULARIO A 18 de mayo de 2005 APELLIDOS NOMBRE CEDULA GRUPO 1. En
UNIVERSIDAD DE LA REPUBLICA. FACULTAD DE MEDICINA CICLO DE ESTRUCTURAS Y FUNCIONES NORMALES UTI "BIOLOGIA TISULAR" ENTREGA MODULO III FORMULARIO A 18 de mayo de 2005 APELLIDOS NOMBRE CEDULA GRUPO 1. En
CATEDRA DE MICROBIOLOGIA. y PARASITOLOGIA FOUBA
 RESPUESTA INMUNE INNATA o NATURAL RECONOCIMIENTO DE PATOGENOS PATRONES MOLECULARES ASOCIADOS A PATOGENOS (PMAP) SE ENCUENTRAN EN EL MICROORGANISMO SON ESENCIALES PARA LA PATOGENICIDAD DE LOS MICROORGANISMOS
RESPUESTA INMUNE INNATA o NATURAL RECONOCIMIENTO DE PATOGENOS PATRONES MOLECULARES ASOCIADOS A PATOGENOS (PMAP) SE ENCUENTRAN EN EL MICROORGANISMO SON ESENCIALES PARA LA PATOGENICIDAD DE LOS MICROORGANISMOS
Células y Tejidos del Sistema Inmunitario. Dra. Liliana Rivas
 Células y Tejidos del Sistema Inmunitario Dra. Liliana Rivas CONTENIDO 1.- Características generales de las células y órganos del sistema inmune. 2.- Funciones y características fenotípicas de: 1) Células
Células y Tejidos del Sistema Inmunitario Dra. Liliana Rivas CONTENIDO 1.- Características generales de las células y órganos del sistema inmune. 2.- Funciones y características fenotípicas de: 1) Células
Componentes humorales de la inmunidad innata
 Componentes humorales de la inmunidad innata INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes INMUNIDAD INNATA Respuesta rápida a un gran espectro de microrganismos INMUNIDAD ACQUIRED IMMUNITY
Componentes humorales de la inmunidad innata INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes INMUNIDAD INNATA Respuesta rápida a un gran espectro de microrganismos INMUNIDAD ACQUIRED IMMUNITY
Inmunología Básica 2017 Departamento de Salud Animal y Medicina Preventiva (SAMP)
 Inmunología Básica 2017 Departamento de Salud Animal y Medicina Preventiva (SAMP) Responsable del curso: Paula Lucchesi, Ing. Agr., Dr Integrantes del curso: Guillermo Arroyo, M. V. Silvia Estein, M. V.
Inmunología Básica 2017 Departamento de Salud Animal y Medicina Preventiva (SAMP) Responsable del curso: Paula Lucchesi, Ing. Agr., Dr Integrantes del curso: Guillermo Arroyo, M. V. Silvia Estein, M. V.
Sangre LA SANGRE. Blgo. Yury Cruzado Torres
 LA SANGRE Blgo. Yury Cruzado Torres Qué es la sangre? La SANGRE, es un tejido circulatorio conectivo especializado, compuesto por plasma sanguíneo y células. Las FUNCIONES de la sangre son: proveer nutrientes
LA SANGRE Blgo. Yury Cruzado Torres Qué es la sangre? La SANGRE, es un tejido circulatorio conectivo especializado, compuesto por plasma sanguíneo y células. Las FUNCIONES de la sangre son: proveer nutrientes
SANGRE Y MÉDULA ÓSEA
 Y MÉDULA ÓSEA Docente: Prof. Adj. Juan Daniel Fernández Hematopoyesis Proceso de formación, diferenciación y desarrollo de las células sanguíneas. Médula ósea Eritrocitos Granulocitos Monocitos Plaquetas
Y MÉDULA ÓSEA Docente: Prof. Adj. Juan Daniel Fernández Hematopoyesis Proceso de formación, diferenciación y desarrollo de las células sanguíneas. Médula ósea Eritrocitos Granulocitos Monocitos Plaquetas
RECOMENDACIONES PARA LA INTERPRETACIÓN DEL FROTIS SANGUÍNEO EN MORFOLOGÍA HEMATOLÓGICA
 Noviembre de 2011 RECOMENDACIONES PARA LA INTERPRETACIÓN DEL FROTIS SANGUÍNEO EN MORFOLOGÍA HEMATOLÓGICA SERIE BLANCA VERSIÓN 011 Laboratorio Nacional de Referencia de Hematología versión 011 hemograma
Noviembre de 2011 RECOMENDACIONES PARA LA INTERPRETACIÓN DEL FROTIS SANGUÍNEO EN MORFOLOGÍA HEMATOLÓGICA SERIE BLANCA VERSIÓN 011 Laboratorio Nacional de Referencia de Hematología versión 011 hemograma
QUÉ ES? QUÉ TIENE? QUÉ HACE?
 QUÉ ES? QUÉ TIENE? E QUÉ HACE? TRANSPORTA: Gases Respiratorios Nutrientes Sustancias Reguladoras Desechos Metabólicos Medicamentos OTRAS: Termoregulación Defensa Equilibrio Ácido-Básico Equilibrio Osmótico
QUÉ ES? QUÉ TIENE? E QUÉ HACE? TRANSPORTA: Gases Respiratorios Nutrientes Sustancias Reguladoras Desechos Metabólicos Medicamentos OTRAS: Termoregulación Defensa Equilibrio Ácido-Básico Equilibrio Osmótico
Sangre. Como parte del tejido conectivo esta formada por células y substancia intercelular llamada plasma
 Sangre Sangre Como parte del tejido conectivo esta formada por células y substancia intercelular llamada plasma Las células sanguíneas se dividen en: 1. Glóbulos rojos 2. Glóbulos blancos 3. Plaquetas
Sangre Sangre Como parte del tejido conectivo esta formada por células y substancia intercelular llamada plasma Las células sanguíneas se dividen en: 1. Glóbulos rojos 2. Glóbulos blancos 3. Plaquetas
CITOLOGÍA E HISTOLOGÍA VETERINARIA
 Tema 12. Sangre: concepto, generalidades y composición. Eritropoyesis. Morfología y función del eritrocito. Trombocitopoyesis. Morfología y función de las plaquetas. Granulocitopoyesis. Características
Tema 12. Sangre: concepto, generalidades y composición. Eritropoyesis. Morfología y función del eritrocito. Trombocitopoyesis. Morfología y función de las plaquetas. Granulocitopoyesis. Características
cecilia gonzález chávez
 cecilia gonzález chávez ph 7.4 Viscoso, color rojo brillante a oscuro 7% peso corporal 5 L en el adulto GENERALIDADES Tejido conectivo especializado Glóbulos rojos Glóbulos blancos Plasma Plaquetas FUNCIONES
cecilia gonzález chávez ph 7.4 Viscoso, color rojo brillante a oscuro 7% peso corporal 5 L en el adulto GENERALIDADES Tejido conectivo especializado Glóbulos rojos Glóbulos blancos Plasma Plaquetas FUNCIONES
25 Inflamación A. Celada
 25 Inflamación A. Celada INTRODUCCIÓN Cuando se produce una rotura de la piel o de las mucosas, los microorganismos pueden pasar del medio externo al interno. Como reacción y en un intento de localizar
25 Inflamación A. Celada INTRODUCCIÓN Cuando se produce una rotura de la piel o de las mucosas, los microorganismos pueden pasar del medio externo al interno. Como reacción y en un intento de localizar
Tipos celulares EOSINO FILO
 Atlas de Histologı a Vegetal y Animal Tipos celulares EOSINO FILO Manuel Megı as, Pilar Molist, Manuel A. Pombal Departamento de Biologı a Funcional y Ciencias de la Salud. Fcacultad de Biologı a. Universidad
Atlas de Histologı a Vegetal y Animal Tipos celulares EOSINO FILO Manuel Megı as, Pilar Molist, Manuel A. Pombal Departamento de Biologı a Funcional y Ciencias de la Salud. Fcacultad de Biologı a. Universidad
FOSFATASA ALCALINA GRANULOCÍTICA
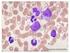 Citoquímica II 2016 LMC FOSFATASA ALCALINA GRANULOCÍTICA Hidroliza monoésteres del ácido fosfórico a ph alcalino (9,1-9,6) Marcadora de la granulación específica de los neutrófilos. Actividad asociada
Citoquímica II 2016 LMC FOSFATASA ALCALINA GRANULOCÍTICA Hidroliza monoésteres del ácido fosfórico a ph alcalino (9,1-9,6) Marcadora de la granulación específica de los neutrófilos. Actividad asociada
SISTEMA CIRCULATORIO: ANATOMÍA. Dra Susana Jerez Cátedra de Anatomía y Fisiología Humana
 SISTEMA CIRCULATORIO: ANATOMÍA Dra Susana Jerez Cátedra de Anatomía y Fisiología Humana Sistema Cardiovascular Está formado por un órgano central con capacidad de impulsar: el corazón, junto a una serie
SISTEMA CIRCULATORIO: ANATOMÍA Dra Susana Jerez Cátedra de Anatomía y Fisiología Humana Sistema Cardiovascular Está formado por un órgano central con capacidad de impulsar: el corazón, junto a una serie
Tejido Conjuntivo TEJIDO CONJUNTIVO. Constituyentes y variedades. Curso Biología Celular y Tisular, Componentes:
 Universidad de la República Facultad de Medicina Escuelas de Tecnología Médica Tejido Conjuntivo Constituyentes y variedades Componentes: Células del tejido conjuntivo. Matriz extracelular (Sustancia fundamental
Universidad de la República Facultad de Medicina Escuelas de Tecnología Médica Tejido Conjuntivo Constituyentes y variedades Componentes: Células del tejido conjuntivo. Matriz extracelular (Sustancia fundamental
El Sistema Inmune. Todos nos vamos enfermar alguna vez.pero luego nos mejoramos. Factores. Factor Ave. Patógeno. Factores Ambientales !
 Factor Ave Nutrición Genética Reproductores Aves Patógeno Factores Patógeno Virulencia Cantidad Genética Factores Ambientales Galpones Temperatura Agua / Cama Ambiental!" # $ % &! ' # ( %% El Sistema Inmune
Factor Ave Nutrición Genética Reproductores Aves Patógeno Factores Patógeno Virulencia Cantidad Genética Factores Ambientales Galpones Temperatura Agua / Cama Ambiental!" # $ % &! ' # ( %% El Sistema Inmune
MC. Edgar Alejandro Turrubiartes Martínez Serie blanca
 Serie blanca Caso 1 La enfermera de una universidad llevó a una estudiante de primer año de 18 años de edad a la sala de urgencia por dolor abdominal interno. No tenía antecedente de enfermedades previas,
Serie blanca Caso 1 La enfermera de una universidad llevó a una estudiante de primer año de 18 años de edad a la sala de urgencia por dolor abdominal interno. No tenía antecedente de enfermedades previas,
TEJIDO CONJUNTIVO. Generalidades. Composición Células Matriz extracelular
 Clase I TEJIDO CONJUNTIVO TEJIDO CONJUNTIVO Generalidades Composición Células Matriz extracelular Células del tejido conjuntivo Residentes (fijas): fibroblastos células reticulares células mesenquimáticas
Clase I TEJIDO CONJUNTIVO TEJIDO CONJUNTIVO Generalidades Composición Células Matriz extracelular Células del tejido conjuntivo Residentes (fijas): fibroblastos células reticulares células mesenquimáticas
COMPLEMENTO El sistema del complemento es el mediador humoral primario de las reacciones antígeno-anticuerpo anticuerpo. Está compuesto por más de 30
 COMPLEMENTO Dr. Carlos R. Kunzle COMPLEMENTO El sistema del complemento es el mediador humoral primario de las reacciones antígeno-anticuerpo anticuerpo. Está compuesto por más de 30 proteínas en el plasma
COMPLEMENTO Dr. Carlos R. Kunzle COMPLEMENTO El sistema del complemento es el mediador humoral primario de las reacciones antígeno-anticuerpo anticuerpo. Está compuesto por más de 30 proteínas en el plasma
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL AUTONOMA DE MEXICO FACULTAD DE ESTUDIOS SUPERIORES IZTACALA CARRERA DE BIOLOGIA SERVICIO SOCIAL SÓCRATES AVILÉS VÁZQUEZ
 UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL AUTONOMA DE MEXICO FACULTAD DE ESTUDIOS SUPERIORES IZTACALA CARRERA DE BIOLOGIA SERVICIO SOCIAL SÓCRATES AVILÉS VÁZQUEZ LAS CÉLULAS DEL SISTEMA INMUNE Los linfocitos cooperadores se
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL AUTONOMA DE MEXICO FACULTAD DE ESTUDIOS SUPERIORES IZTACALA CARRERA DE BIOLOGIA SERVICIO SOCIAL SÓCRATES AVILÉS VÁZQUEZ LAS CÉLULAS DEL SISTEMA INMUNE Los linfocitos cooperadores se
Inmunología. Presentación montada con fines didáctico por José Antonio Pascual Trillo (IES El Escorial)
 Inmunología EL SISTEMA INMUNITARIO ( 2 ) : LA RESPUESTA INMUNE Presentación montada con fines didáctico por José Antonio Pascual Trillo (IES El Escorial) La respuesta inespecífica o innata es la primera
Inmunología EL SISTEMA INMUNITARIO ( 2 ) : LA RESPUESTA INMUNE Presentación montada con fines didáctico por José Antonio Pascual Trillo (IES El Escorial) La respuesta inespecífica o innata es la primera
Citología de la médula ósea y sangre
 Citología de la médula ósea y sangre Cristina Fernández Algarra Diagnóstico citológico veterinario. Avenida del Padre Piquer 4. 28024-Madrid. cf.algarra@telefonica.net Resumen: en la médula ósea se generan
Citología de la médula ósea y sangre Cristina Fernández Algarra Diagnóstico citológico veterinario. Avenida del Padre Piquer 4. 28024-Madrid. cf.algarra@telefonica.net Resumen: en la médula ósea se generan
María Romero Sánchez. http://agaudi.files.wordpress.com/2009/03/david-gregorydebbie-marshallcelulas-sanguineas-en-un-coagulo.jpg
 María Romero Sánchez http://agaudi.files.wordpress.com/2009/03/david-gregorydebbie-marshallcelulas-sanguineas-en-un-coagulo.jpg La sangre es un tejido formado por diversas células suspendidas (45%) en
María Romero Sánchez http://agaudi.files.wordpress.com/2009/03/david-gregorydebbie-marshallcelulas-sanguineas-en-un-coagulo.jpg La sangre es un tejido formado por diversas células suspendidas (45%) en
Introducción de la practica de Tejido Conectivo General (TCG).
 Introducción de la practica de Tejido Conectivo General (TCG). Para el estudio microscópico del tejido conectivo general debemos tener claros algunos aspectos: Es un tejido cuyas células están muy separadas
Introducción de la practica de Tejido Conectivo General (TCG). Para el estudio microscópico del tejido conectivo general debemos tener claros algunos aspectos: Es un tejido cuyas células están muy separadas
Dos tipos de DEFENSAS: 1.- EXTERNAS O PASIVAS: 2.- INESPECÍFICAS: - Estructurales - Mecánicas - Bioquímicas - Ecológicas
 (Inmunología I) Dos tipos de DEFENSAS: 1.- EXTERNAS O PASIVAS: - Estructurales - Mecánicas - Bioquímicas - Ecológicas 2.- INESPECÍFICAS: - Inflamación - Fagocitos (respuesta celular) - Inmune (respuesta
(Inmunología I) Dos tipos de DEFENSAS: 1.- EXTERNAS O PASIVAS: - Estructurales - Mecánicas - Bioquímicas - Ecológicas 2.- INESPECÍFICAS: - Inflamación - Fagocitos (respuesta celular) - Inmune (respuesta
CURSO DE MORFOLOGÍA HEMATOLÓGICA
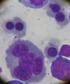 CURSO DE MORFOLOGÍA HEMATOLÓGICA Caracas, 10 de julio de 2015 Caso Clínico I.A.H.U.L.A. Mérida Alexander Manuel Arellano Rojas Médico Residente de Hematología de la ULA SOCIEDAD VENEZOLANA DE HEMATOLOGÍA
CURSO DE MORFOLOGÍA HEMATOLÓGICA Caracas, 10 de julio de 2015 Caso Clínico I.A.H.U.L.A. Mérida Alexander Manuel Arellano Rojas Médico Residente de Hematología de la ULA SOCIEDAD VENEZOLANA DE HEMATOLOGÍA
Células y Tejidos del Sistema Inmunitario. Dra. Liliana Rivas
 Células y Tejidos del Sistema Inmunitario Dra. Liliana Rivas CONTENIDO 1.- Características generales de las células y órganos del sistema inmune. 2.- Funciones y características fenotípicas de: 1) Células
Células y Tejidos del Sistema Inmunitario Dra. Liliana Rivas CONTENIDO 1.- Características generales de las células y órganos del sistema inmune. 2.- Funciones y características fenotípicas de: 1) Células
Centro de Microscopía Electrónica LISOSOMAS - PEROXISOMAS
 LISOSOMAS - PEROXISOMAS SÍNTESIS PROTEICA En células hepáticas de rata, los peroxisomas son reconocidos por la presencia de un depósito cristalino central de urato oxidasa. En humanos este depósito cristalino
LISOSOMAS - PEROXISOMAS SÍNTESIS PROTEICA En células hepáticas de rata, los peroxisomas son reconocidos por la presencia de un depósito cristalino central de urato oxidasa. En humanos este depósito cristalino
FACULTAD DE CIENCIAS QUIMICAS UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA DE CHIAPAS MATERIAL PARA LA MATERIA DE: HEMATOLOGIA UNIDAD VII LEUCOCITOS CATEDRATICO TITULAR:
 MATERIAL PARA LA MATERIA DE: HEMATOLOGIA UNIDAD VII LEUCOCITOS CATEDRATICO TITULAR: DRA EN C. CONSUELO CHANG RUEDA TC. TITULAR " B " CICLO ESCOLAR: ENERO DICIEMBRE DEL 2015 Tapachula, Chis México. 1 Í
MATERIAL PARA LA MATERIA DE: HEMATOLOGIA UNIDAD VII LEUCOCITOS CATEDRATICO TITULAR: DRA EN C. CONSUELO CHANG RUEDA TC. TITULAR " B " CICLO ESCOLAR: ENERO DICIEMBRE DEL 2015 Tapachula, Chis México. 1 Í
14/11/2011. Ana María Ramírez Kamann, MV Unidad Patología Clínica 2011
 Universidad de Chile Facultad de Ciencias Veterinarias y Pecuarias Departamento de Patología Animal Desórdenes Leucocitarios Ana María Ramírez Kamann, MV Unidad Patología Clínica 2011 anramire@uchile.cl
Universidad de Chile Facultad de Ciencias Veterinarias y Pecuarias Departamento de Patología Animal Desórdenes Leucocitarios Ana María Ramírez Kamann, MV Unidad Patología Clínica 2011 anramire@uchile.cl
Congreso Nacional del Laboratorio Clínico 2015
 CITOLOGÍA DE SANGRE PERIFÉRICA Y AUTOMATIZACIÓN EN EL DIAGNÓSTICO DE LAS ENFERMEDADES HEMATOLÓGICAS MALIGNAS 8 de Octubre del 2015 Cristian Morales-Indiano AUTOMATIZACIÓN Changing the EN conversation HEMATIMETRIA.
CITOLOGÍA DE SANGRE PERIFÉRICA Y AUTOMATIZACIÓN EN EL DIAGNÓSTICO DE LAS ENFERMEDADES HEMATOLÓGICAS MALIGNAS 8 de Octubre del 2015 Cristian Morales-Indiano AUTOMATIZACIÓN Changing the EN conversation HEMATIMETRIA.
GUÍA DE TRABAJOS PRÁCTICOS Nº2. Hemograma. Recuento diferencial leucocitario. Trastornos leucocitarios.
 Facultad de Bioquímica, Química y Farmacia Universidad Nacional de Tucumán GUÍA DE TRABAJOS PRÁCTICOS Nº2 Hemograma. Recuento diferencial leucocitario. Trastornos leucocitarios. 1 RECUENTO DIFERENCIAL
Facultad de Bioquímica, Química y Farmacia Universidad Nacional de Tucumán GUÍA DE TRABAJOS PRÁCTICOS Nº2 Hemograma. Recuento diferencial leucocitario. Trastornos leucocitarios. 1 RECUENTO DIFERENCIAL
SISTEMA DEL COMPLEMENTO
 UNIVERSIDAD DE SAN CARLOS DE GUATEMALA FACULTAD DE CIENCIAS MÉDICAS M FASE I, Unidad Didáctica: BIOQUÍMICA MÉDICA M 2º 2 AÑO SISTEMA DEL COMPLEMENTO Dr. Mynor A. Leiva Enríquez En el eje vertical con la
UNIVERSIDAD DE SAN CARLOS DE GUATEMALA FACULTAD DE CIENCIAS MÉDICAS M FASE I, Unidad Didáctica: BIOQUÍMICA MÉDICA M 2º 2 AÑO SISTEMA DEL COMPLEMENTO Dr. Mynor A. Leiva Enríquez En el eje vertical con la
PROPIEDADES Y FUNCIONES DE LOS GRANULOCITOS
 PROPIEDADES Y FUNCIONES DE LOS GRANULOCITOS Cátedra de Hematología Dra Pérez Susana M Año 2015 1 PROPIEDADES Y FUNCIONES DE LOS GRANULOCITOS: DEFINICIÓN: Se denomina granulocitos a los leucocitos que poseen
PROPIEDADES Y FUNCIONES DE LOS GRANULOCITOS Cátedra de Hematología Dra Pérez Susana M Año 2015 1 PROPIEDADES Y FUNCIONES DE LOS GRANULOCITOS: DEFINICIÓN: Se denomina granulocitos a los leucocitos que poseen
Leucocitosis y Leucopenia: Diagnostico diferencial
 Leucocitosis y Leucopenia: Diagnostico diferencial Dra. Carolina Tokumura Jefe del Servicio de Hematología-Oncología Clínica Hospital Cayetano Heredia Profesor Auxiliar Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia
Leucocitosis y Leucopenia: Diagnostico diferencial Dra. Carolina Tokumura Jefe del Servicio de Hematología-Oncología Clínica Hospital Cayetano Heredia Profesor Auxiliar Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia
TEMA 16.- SEPSIS. La sepsis es una respuesta inflamatoria del organismo (SIRS) ante una infección.
 TEMA 16.- SEPSIS Dr. Juan C. Montejo La sepsis es una respuesta inflamatoria del organismo (SIRS) ante una infección. Cada pocos segundos alguien fallece por sepsis en el mundo. La sepsis es una de las
TEMA 16.- SEPSIS Dr. Juan C. Montejo La sepsis es una respuesta inflamatoria del organismo (SIRS) ante una infección. Cada pocos segundos alguien fallece por sepsis en el mundo. La sepsis es una de las
Asma Bronquial. Mg. Marta Giacomino - SPM - Lic. en Klgía y Fisiatría - FCS - UNER
 Asma Bronquial enfermedad inflamatoria de las vías aéreas a la que se asocia intensa hiperreactividad bronquial frente a estímulos diversos. Actuando conjuntamente, ambos fenómenos ocasionan la obstrucción
Asma Bronquial enfermedad inflamatoria de las vías aéreas a la que se asocia intensa hiperreactividad bronquial frente a estímulos diversos. Actuando conjuntamente, ambos fenómenos ocasionan la obstrucción
II CURSO DE DIAGNÓSTICO INTEGRAL EN HEMATOLOGÍA. Módulo 4. Dr. Joaquín Carrillo Farga Instituto de Hematopatología de México.
 II CURSO DE DIAGNÓSTICO INTEGRAL EN HEMATOLOGÍA. Módulo 4 Dr. Joaquín Carrillo Farga Instituto de Hematopatología de México. Queretaro, México Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal Salón de Actos: 27 y
II CURSO DE DIAGNÓSTICO INTEGRAL EN HEMATOLOGÍA. Módulo 4 Dr. Joaquín Carrillo Farga Instituto de Hematopatología de México. Queretaro, México Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal Salón de Actos: 27 y
Células pequeñas 1 10 µm Células de mayor tamaño; µm
 La Célula REPASO La Célula - Repaso Diferencias entre célula procariota y eucariota Diferencias entre célula animal y vegetal Membrana celular Estructura Funciones Citoplasma Hialoplasma (composición)
La Célula REPASO La Célula - Repaso Diferencias entre célula procariota y eucariota Diferencias entre célula animal y vegetal Membrana celular Estructura Funciones Citoplasma Hialoplasma (composición)
Células pequeñas 1 10 µm Células de mayor tamaño; µm
 La Célula REPASO La Célula - Repaso Diferencias entre célula procariota y eucariota Diferencias entre célula animal y vegetal Membrana celular Estructura Funciones Citoplasma Hialoplasma (composición)
La Célula REPASO La Célula - Repaso Diferencias entre célula procariota y eucariota Diferencias entre célula animal y vegetal Membrana celular Estructura Funciones Citoplasma Hialoplasma (composición)
Prácticas: Configuración de los seres vivos. Curso académico Práctica 2. Preparación de extensiones celulares.
 Prácticas: Configuración de los seres vivos. Curso académico 2009-2010 16 Práctica 2. Preparación de extensiones celulares Introducción Se entiende por extensión o frotis celular, a la formación de una
Prácticas: Configuración de los seres vivos. Curso académico 2009-2010 16 Práctica 2. Preparación de extensiones celulares Introducción Se entiende por extensión o frotis celular, a la formación de una
GENERALIDADES DE LA RESPUESTA INMUNE
 GENERALIDADES DE LA RESPUESTA INMUNE 1 BACTERIAS REPLICACION EXTRACELULAR REPLICACION INTRACELULAR Neumococo Mycobacterium tuberculosis VIRUS 2 Parásitos Helmintos Protozoos Taenia Tripanosoma Crusi Hongos
GENERALIDADES DE LA RESPUESTA INMUNE 1 BACTERIAS REPLICACION EXTRACELULAR REPLICACION INTRACELULAR Neumococo Mycobacterium tuberculosis VIRUS 2 Parásitos Helmintos Protozoos Taenia Tripanosoma Crusi Hongos
Componentes humorales de la inmunidad innata. Dra. Claudia Lützelschwab Departamento de Sanidad Animal y Medicina Preventiva
 Componentes humorales de la inmunidad innata Dra. Claudia Lützelschwab Departamento de Sanidad Animal y Medicina Preventiva Clase anterior...células efectoras de la Inmunidad Innata SANGRE Eosinófilos
Componentes humorales de la inmunidad innata Dra. Claudia Lützelschwab Departamento de Sanidad Animal y Medicina Preventiva Clase anterior...células efectoras de la Inmunidad Innata SANGRE Eosinófilos
MATERIAL DIDÁCTICO PARA ENSEÑAR Y APRENDER EL DIAGNÓSTICO CITOMORFOLÓGICO DE LAS CELULAS HEMÁTICAS.
 MATERIAL DIDÁCTICO PARA ENSEÑAR Y APRENDER EL DIAGNÓSTICO CITOMORFOLÓGICO DE LAS CELULAS HEMÁTICAS. Sierra Salcedo Carlos 1, Cuellar Jiménez Paulina 1, Garduño Islas Alma Rocío 1, Valle Moreno Marcela
MATERIAL DIDÁCTICO PARA ENSEÑAR Y APRENDER EL DIAGNÓSTICO CITOMORFOLÓGICO DE LAS CELULAS HEMÁTICAS. Sierra Salcedo Carlos 1, Cuellar Jiménez Paulina 1, Garduño Islas Alma Rocío 1, Valle Moreno Marcela
Linfocitos T e inmunidad celular. Inmunidad humoral.
 Linfocitos T e inmunidad celular. Inmunidad humoral. García Servicio de Alergología H.U.V.A - Murcia La inmunidad o respuesta inmune es la respuesta a sustancias extrañas (antígenos), incluyendo microorganismos,
Linfocitos T e inmunidad celular. Inmunidad humoral. García Servicio de Alergología H.U.V.A - Murcia La inmunidad o respuesta inmune es la respuesta a sustancias extrañas (antígenos), incluyendo microorganismos,
Inflamación (3) MEDIADORES QUIMICOS DE LA INFLAMACION. Lo que se comprende en un abrir y cerrar de ojos, no suele dejar huella (Andre Gide)
 Inflamación (3) MEDIADORES QUIMICOS DE LA INFLAMACION Lo que se comprende en un abrir y cerrar de ojos, no suele dejar huella (Andre Gide) Mediadores químicos de inflamación Premisas Moléculas que participan
Inflamación (3) MEDIADORES QUIMICOS DE LA INFLAMACION Lo que se comprende en un abrir y cerrar de ojos, no suele dejar huella (Andre Gide) Mediadores químicos de inflamación Premisas Moléculas que participan
SISTEMA SISTEM INMUNE
 CONDICIÓN DEL SISTEMA INMUNE DEL RECIÉN NACIDO PROFESOR MTRN. SERGIO PAVIÉ CORONADO ENFM-121 2009 GENERALIDADES I SISTEMA INMUNE DEL RN El Sistema Inmunológico es un conjunto de estructuras anatómicas,
CONDICIÓN DEL SISTEMA INMUNE DEL RECIÉN NACIDO PROFESOR MTRN. SERGIO PAVIÉ CORONADO ENFM-121 2009 GENERALIDADES I SISTEMA INMUNE DEL RN El Sistema Inmunológico es un conjunto de estructuras anatómicas,
Inflamación, Daño y Reparación en Enfermedades Reumáticas
 Medwave. Año VIII, No. 6, Julio 2008. Derechos Reservados Inflamación, Daño y Reparación en Enfermedades Reumáticas Dra. María Angélica Marinovic M. Sección Inmunología y Alergología, Hospital Clínico
Medwave. Año VIII, No. 6, Julio 2008. Derechos Reservados Inflamación, Daño y Reparación en Enfermedades Reumáticas Dra. María Angélica Marinovic M. Sección Inmunología y Alergología, Hospital Clínico
Tema 5.- Respuesta innata II. Fagocitosis. Complemento
 Tema 5.- Respuesta innata II. Fagocitosis. Complemento Principales características Descubierto por Bordet en 1895 Sistema de mas de 30 proteínas que actúan an de modo secuencial Sintetizadas por los hepatocitos
Tema 5.- Respuesta innata II. Fagocitosis. Complemento Principales características Descubierto por Bordet en 1895 Sistema de mas de 30 proteínas que actúan an de modo secuencial Sintetizadas por los hepatocitos
TEJIDO SANGUINEO DRA. ALEJANDRA B. QUINTANA
 TEJIDO SANGUINEO DRA. ALEJANDRA B. QUINTANA 2016 TEJIDO SANGUINEO La sangre es un tejido conjuntivo líquido que circula por el aparato cardiovascular COMPOSICIÓN DEL TEJIDO SANGUÍNEO: La sangre es un fluido
TEJIDO SANGUINEO DRA. ALEJANDRA B. QUINTANA 2016 TEJIDO SANGUINEO La sangre es un tejido conjuntivo líquido que circula por el aparato cardiovascular COMPOSICIÓN DEL TEJIDO SANGUÍNEO: La sangre es un fluido
MECANISMOS DE AMPLIFICACIÓN DE LA RESPUESTA INMUNE. Dra Morella Bouchard IDIC-ULA
 MECANISMOS DE AMPLIFICACIÓN DE LA RESPUESTA INMUNE Dra Morella Bouchard IDIC-ULA INMUNIDAD INNATA PRIMERA LÍNEA DE DEFENSA CONTRA LAS INFECCIONES La inmunidad innata estimula la respuesta inmunitaria adaptativa
MECANISMOS DE AMPLIFICACIÓN DE LA RESPUESTA INMUNE Dra Morella Bouchard IDIC-ULA INMUNIDAD INNATA PRIMERA LÍNEA DE DEFENSA CONTRA LAS INFECCIONES La inmunidad innata estimula la respuesta inmunitaria adaptativa
MACRÓFAGOS O HISTIOCITOS.
 En las microfotografías electrónicas las células cebadas muestran numerosos repliegues de la superficie celular. El Aparato de Golgi está bien desarrollado; sin embargo, el retículo endoplásmico y las
En las microfotografías electrónicas las células cebadas muestran numerosos repliegues de la superficie celular. El Aparato de Golgi está bien desarrollado; sin embargo, el retículo endoplásmico y las
1.Elementos figurados
 1.Elementos figurados Componentes sanguíneos * Glóbulos rojos o eritrocitos * Glóbulos blancos o leucocitos Granulocitos Neutrofilos Eosinofilos Basofilos * Plaquetas o trombocitos Agranulocitos. Enfermero
1.Elementos figurados Componentes sanguíneos * Glóbulos rojos o eritrocitos * Glóbulos blancos o leucocitos Granulocitos Neutrofilos Eosinofilos Basofilos * Plaquetas o trombocitos Agranulocitos. Enfermero
Hematología. Unidad 8
 UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA DE CHIAPAS FACULTAD DE CIENCIAS QUIMICAS APUNTES IMPRESOS DE LA MATERIA DE : Hematología Unidad 8 Interpretación de la formula blanca, leucocitosis y leucemias CICLO : ENERO DICIEMBRE
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA DE CHIAPAS FACULTAD DE CIENCIAS QUIMICAS APUNTES IMPRESOS DE LA MATERIA DE : Hematología Unidad 8 Interpretación de la formula blanca, leucocitosis y leucemias CICLO : ENERO DICIEMBRE
Propiedades y funciones generales de la sangre. T.M. Pamela Carmona Rios Instituto de Fisiología
 Propiedades y funciones generales de la sangre T.M. Pamela Carmona Rios Instituto de Fisiología Qué es la sangre? La Sangre es una forma especializada de tejido conectivo que consiste de elementos figurados
Propiedades y funciones generales de la sangre T.M. Pamela Carmona Rios Instituto de Fisiología Qué es la sangre? La Sangre es una forma especializada de tejido conectivo que consiste de elementos figurados
INFLAMACIÓN CRÓNICA 08/03/2013. Dr. José M. Cameselle Teijeiro Departamento de Anatomía Patológica Curso INFLAMACIÓN AGUDA
 INFLAMACIÓN Es una respuesta protectora tisular destinada a eliminar tanto la causa inicial de la lesión celular, como las células y los tejidos necróticos debidos a la agresión inicial. (reacción de los
INFLAMACIÓN Es una respuesta protectora tisular destinada a eliminar tanto la causa inicial de la lesión celular, como las células y los tejidos necróticos debidos a la agresión inicial. (reacción de los
Bibliografía básica correspondiente a la respuesta inmunitaria
 Sistema Inmune Bibliografía básica correspondiente a la respuesta inmunitaria - Curtis, H y otros. Biología. Buenos Aires, Panamericana, 7º edición, Sección 6. Cap. 40 (pág. 754-771) - Horacio E. Cingolani-Alberto
Sistema Inmune Bibliografía básica correspondiente a la respuesta inmunitaria - Curtis, H y otros. Biología. Buenos Aires, Panamericana, 7º edición, Sección 6. Cap. 40 (pág. 754-771) - Horacio E. Cingolani-Alberto
AUTOEVALUACION DE HEMATOLOGIA
 FACULTAD DE MEDICINA CICLO DE ESTRUCTURAS Y FUNCIONES NORMALES UTI "BIOLOGIA TISULAR" AUTOEVALUACION DE HEMATOLOGIA 1.- Con respecto a las células sanguíneas indique la o las opciones correctas: a) La
FACULTAD DE MEDICINA CICLO DE ESTRUCTURAS Y FUNCIONES NORMALES UTI "BIOLOGIA TISULAR" AUTOEVALUACION DE HEMATOLOGIA 1.- Con respecto a las células sanguíneas indique la o las opciones correctas: a) La
Fisiología General. Tema 8. Las células, los fagocitos y las APCs
 Tema 8. Las células NK, los fagocitos y las APCs Las células natural killer. Los polimorfonucleares neutrófilos. El sistema monocito- macrófago: - Tipos celulares. - Productos que secretan. - Funciones
Tema 8. Las células NK, los fagocitos y las APCs Las células natural killer. Los polimorfonucleares neutrófilos. El sistema monocito- macrófago: - Tipos celulares. - Productos que secretan. - Funciones
Defectos en Células Fagocíticas y su Diagnóstico. JAIRO MUÑOZ CERÓN MD. Esp. MSc. Fundación Universitaria Sanitas Facultad de Medicina
 Defectos en Células Fagocíticas y su Diagnóstico JAIRO MUÑOZ CERÓN MD. Esp. MSc. Fundación Universitaria Sanitas Facultad de Medicina IDP Incidencia: 1/10,000 (2:1, : ) Distribución: 5% 10% 5% Humorales
Defectos en Células Fagocíticas y su Diagnóstico JAIRO MUÑOZ CERÓN MD. Esp. MSc. Fundación Universitaria Sanitas Facultad de Medicina IDP Incidencia: 1/10,000 (2:1, : ) Distribución: 5% 10% 5% Humorales
MECANISMOS DE AMPLIFICACIÓN DE LA RESPUESTA INMUNOLÓGICA. José Angel Cova, MD
 MECANISMOS DE AMPLIFICACIÓN DE LA RESPUESTA INMUNOLÓGICA José Angel Cova, MD jacova@ula.ve INMUNIDAD INNATA MECANISMOS DE DEFENSA ACTIVOS PREVIO AL ENCUENTRO CON EL ANTÍGENO SON MECANISMOS NO MODIFICADOS
MECANISMOS DE AMPLIFICACIÓN DE LA RESPUESTA INMUNOLÓGICA José Angel Cova, MD jacova@ula.ve INMUNIDAD INNATA MECANISMOS DE DEFENSA ACTIVOS PREVIO AL ENCUENTRO CON EL ANTÍGENO SON MECANISMOS NO MODIFICADOS
